Trading Features on Exchanges: Complete 2025 Guide
Trading features on cryptocurrency exchanges have evolved dramatically, offering sophisticated tools and diverse trading options that cater to both novice investors and professional traders. Modern crypto exchanges provide comprehensive trading ecosystems encompassing spot trading, margin trading, futures contracts, options trading, and advanced order management systems that enable traders to execute complex strategies efficiently.
The cryptocurrency trading landscape in 2025 features ultra-low latency execution engines, advanced algorithmic trading capabilities, cross-margin systems, and institutional-grade risk management tools. Leading exchanges like Binance, Bybit, OKX, and Gate.io compete through innovative features, competitive fee structures, and comprehensive trading environments.
This comprehensive guide explores the essential trading features available on cryptocurrency exchanges, from basic spot trading to advanced derivatives strategies. You will discover how different trading features work, their benefits and risks, and which platforms offer the best tools for your trading objectives and experience level.
Spot Trading: The Foundation of Crypto Trading
Spot trading represents the most fundamental and widely used trading feature on cryptocurrency exchanges, involving the immediate purchase and sale of digital assets at current market prices.
Core Spot Trading Mechanics
Spot trading provides direct ownership of cryptocurrencies with immediate settlement, making it the preferred choice for beginners and long-term investors seeking actual asset ownership.
Immediate Settlement: Trades execute instantly at prevailing market prices, with immediate transfer of asset ownership to the buyer’s account. This eliminates counterparty risk associated with derivative products.
Asset Ownership: Unlike derivatives trading, spot trading provides actual cryptocurrency ownership, allowing users to withdraw assets to personal wallets, participate in staking, or use tokens in decentralized applications.
Price Transparency: Spot prices reflect real supply and demand dynamics without the complexity of funding rates, expiration dates, or contract specifications found in derivatives markets.
Spot Trading Advantages
The simplicity and transparency of spot trading make it ideal for newcomers to cryptocurrency markets and risk-averse investors.
Low Risk Profile: Losses are limited to the initial investment amount, with no risk of liquidation or margin calls that characterize leveraged trading products.
Regulatory Clarity: Spot trading faces fewer regulatory restrictions compared to margin and derivatives trading, making it accessible in most jurisdictions with basic compliance requirements.
Educational Value: The straightforward buy-low, sell-high approach helps new traders understand market dynamics without complex financial instruments.
Spot Trading Limitations
While spot trading offers simplicity and safety, it provides limited profit amplification opportunities compared to leveraged trading features.
Capital Requirements: Traders need sufficient capital to take meaningful positions, as leverage is not available to amplify buying power.
Limited Strategy Options: Spot trading primarily supports long positions, with limited ability to profit from declining markets without actually owning short-able assets.
Margin Trading: Amplified Trading Power
Margin trading enables traders to borrow funds from exchanges to increase their buying power, amplifying both potential profits and losses through leverage.
Margin Trading Fundamentals
Margin trading allows users to borrow against their existing cryptocurrency holdings to open larger positions than their account balance would normally permit.
Leverage Mechanisms: Most exchanges offer margin leverage ranging from 2x to 10x on spot trades, with some platforms providing up to 125x on specialized margin products.
Collateral Requirements: Traders must maintain minimum collateral ratios, typically ranging from 10% to 50% of the borrowed amount, depending on the asset and exchange policies.
Interest Rates: Borrowed funds incur interest charges, usually calculated hourly or daily, with rates varying based on market demand for specific cryptocurrencies.
Cross Margin vs Isolated Margin
Exchanges typically offer two margin modes with different risk profiles and capital allocation strategies.
Cross Margin Trading: Uses the entire account balance as collateral for all positions, allowing profitable trades to support losing positions but risking the entire account balance.
Isolated Margin Trading: Limits risk to specific position collateral, preventing losses from affecting other positions while requiring individual position management.
Margin Trading Benefits
Margin trading provides enhanced profit potential and strategic flexibility for experienced traders.
Capital Efficiency: Traders can take larger positions with less capital, potentially increasing returns on successful trades through leverage amplification.
Portfolio Diversification: Access to borrowed funds enables traders to diversify across more assets without requiring additional capital deposits.
Short Selling Opportunities: Many margin platforms enable short selling, allowing traders to profit from declining asset prices.
Margin Trading Risks
The amplified potential of margin trading comes with significant risks that require careful consideration and risk management.
Liquidation Risk: If collateral falls below maintenance requirements, exchanges automatically close positions at potentially unfavorable prices to protect lenders.
Interest Costs: Borrowing fees can accumulate quickly, especially for long-term positions, potentially eroding profits or amplifying losses.
Market Volatility Impact: Cryptocurrency price volatility can trigger rapid liquidations, especially with high leverage ratios and insufficient risk management.
Futures Trading: Derivative Contracts for Advanced Strategies
Futures trading involves contracts that derive value from underlying cryptocurrencies without requiring direct asset ownership, enabling sophisticated trading strategies.
Futures Contract Types
Cryptocurrency exchanges offer various futures contract types to accommodate different trading strategies and risk preferences.
Perpetual Futures: Contracts with no expiration date that track underlying spot prices through funding rate mechanisms, popular for their flexibility and continuous trading.
Quarterly Futures: Fixed-expiration contracts settled on specific dates, typically quarterly, offering price discovery for future delivery dates.
Linear vs Inverse Contracts: Linear contracts use stablecoins (USDT/USDC) for margin and settlement, while inverse contracts use the underlying cryptocurrency, affecting profit/loss calculations.
Leverage and Risk Management
Futures trading typically offers higher leverage than margin trading, with sophisticated risk management tools to handle increased exposure.
High Leverage Options: Many exchanges provide leverage up to 125x or even 200x on popular cryptocurrency futures, enabling significant position sizes with minimal capital.
Advanced Order Types: Futures platforms support complex order types including stop-loss, take-profit, trailing stops, and conditional orders for precise risk control.
Liquidation Systems: Automated liquidation engines protect traders and exchanges from adverse price movements by closing positions when margins are insufficient.
Funding Rate Mechanisms
Perpetual futures use funding rates to maintain price convergence with underlying spot markets.
Funding Rate Calculations: Rates are typically calculated every 8 hours based on the premium or discount between futures and spot prices.
Trader Impact: Long position holders pay funding fees when rates are positive, while short holders pay when rates are negative, creating natural price balancing.
Options Trading: Sophisticated Risk Management
Options contracts provide the right, but not obligation, to buy or sell cryptocurrencies at predetermined prices, enabling advanced hedging and speculation strategies.
Options Contract Basics
Cryptocurrency options offer strategic flexibility for both speculation and risk management applications.
Call and Put Options: Call options provide the right to buy assets at strike prices, while put options grant the right to sell, enabling directional and non-directional strategies.
Exercise vs Settlement: Most crypto options are cash-settled rather than requiring physical delivery of underlying cryptocurrencies.
Time Decay Factors: Options lose value as expiration approaches, requiring consideration of time decay in strategy development.
Options Trading Strategies
Advanced traders use options for complex strategies combining multiple contracts for specific risk-reward profiles.
Protective Strategies: Buying put options to hedge long spot positions against downside risk while maintaining upside potential.
Income Generation: Selling covered calls against existing cryptocurrency holdings to generate additional income through premium collection.
Volatility Trading: Strategies like straddles and strangles enable profits from volatility changes regardless of price direction.
Options Pricing and Greeks
Understanding options pricing factors is essential for effective options trading.
Implied Volatility: Market expectations of future price volatility significantly impact option prices, especially for at-the-money options.
Greeks Analysis: Delta, gamma, theta, and vega measure price sensitivity to various factors, helping traders understand risk exposure and profit potential.
Advanced Order Types and Execution Features
Modern cryptocurrency exchanges provide sophisticated order management systems enabling precise trade execution and automated strategy implementation.
Standard Order Types
Basic order types form the foundation of trading execution across all major exchanges.
Market Orders: Execute immediately at current market prices, providing guaranteed fills but potentially unfavorable pricing during volatile conditions.
Limit Orders: Execute only at specified prices or better, providing price control but no guarantee of execution if markets move away from limit prices.
Stop Orders: Trigger market orders when predetermined price levels are reached, useful for loss limitation and breakout strategies.
Advanced Order Management
Professional trading platforms offer sophisticated order types for complex strategy execution.
Stop-Limit Orders: Combine stop triggers with limit order execution, preventing market order slippage while maintaining price protection.
Trailing Stop Orders: Automatically adjust stop prices as markets move favorably, locking in profits while allowing continued upside participation.
Iceberg Orders: Break large orders into smaller portions to minimize market impact and hide trading intentions from other participants.
Bracket Orders: Combine profit-taking and loss-limiting orders with primary positions, automating risk management without constant monitoring.
Algorithmic Trading Features
Advanced exchanges provide API access and algorithmic trading capabilities for systematic strategy execution.
REST and WebSocket APIs: Enable custom trading application development and real-time market data access for algorithmic strategies.
Trading Bots Integration: Many platforms offer built-in trading bot functionality or integration with third-party algorithmic trading services.
Copy Trading Systems: Social trading features allow users to automatically replicate successful traders’ strategies with proportional position sizing.
Risk Management and Security Features
Comprehensive risk management tools are essential for protecting capital and managing exposure across different trading strategies.
Position Risk Controls
Exchanges implement various mechanisms to help traders manage individual position risks.
Position Size Limits: Maximum position sizes prevent excessive exposure to single assets or trading pairs, protecting both traders and exchanges.
Leverage Restrictions: Many platforms implement dynamic leverage limits based on account size, trading history, and market volatility conditions.
Maintenance Margin Requirements: Minimum collateral levels ensure adequate margin coverage, with automatic liquidation when requirements are breached.
Account-Level Protections
Broader account protection mechanisms safeguard against systematic risks and operational issues.
Daily Loss Limits: Some exchanges offer optional daily loss limits to prevent emotional trading and protect against significant account drawdowns.
Withdrawal Restrictions: Time-delayed withdrawals and whitelisted addresses provide additional security against unauthorized account access.
Two-Factor Authentication: Mandatory 2FA for trading and withdrawal functions adds crucial security layers for account protection.
Insurance and Compensation
Leading exchanges provide various forms of user protection against platform risks and operational issues.
Insurance Funds: Exchange-maintained funds cover losses from extreme market movements, system failures, or liquidation shortfalls.
Proof of Reserves: Regular audits and public reporting of exchange asset holdings demonstrate solvency and user fund protection.
Compensation Programs: Some platforms offer limited compensation for losses due to system outages, security breaches, or operational errors.
Fee Structures and Cost Optimization
Understanding exchange fee structures is crucial for optimizing trading costs and maximizing net returns across different trading features.
Trading Fee Models
Most exchanges use maker-taker fee structures with volume-based discounts to encourage liquidity provision and high-volume trading.
Maker-Taker Pricing: Makers who provide liquidity pay lower fees (typically 0.02-0.10%) while takers who remove liquidity pay higher fees (0.05-0.15%).
Volume-Based Discounts: Trading fees decrease as monthly trading volume increases, with VIP programs offering substantial savings for high-volume traders.
Native Token Benefits: Many exchanges offer fee discounts for users holding or using platform native tokens for fee payment.
Specialized Fee Structures
Different trading features often have unique fee structures reflecting their complexity and risk profiles.
Futures Trading Fees: Generally lower than spot trading fees, with maker fees sometimes offering rebates to encourage liquidity provision.
Options Trading Costs: Include both trading fees and potentially higher bid-ask spreads due to lower liquidity in options markets.
Margin Trading Expenses: Combine trading fees with borrowing interest, requiring consideration of total cost of capital for leveraged positions.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Traders can implement various strategies to minimize trading costs across different features.
Fee Tier Management: Strategic trading volume management to achieve lower fee tiers through concentrated trading on preferred exchanges.
Order Type Selection: Using limit orders instead of market orders can qualify for maker fees, reducing trading costs significantly.
Native Token Utilization: Acquiring exchange tokens for fee discounts often provides significant cost savings for active traders.
Platform Comparison: Leading Exchange Features
Understanding how different exchanges implement trading features helps traders choose platforms aligned with their strategies and preferences.
Binance Trading Features
Binance offers the most comprehensive feature set with competitive fees and deep liquidity across all trading types.
Feature Breadth: Supports spot, margin (up to 10x), futures (up to 125x), options, and various specialized products across 600+ cryptocurrencies.
Advanced Tools: Provides professional-grade charting, algorithmic trading APIs, and copy trading features for diverse trading strategies.
Fee Competitiveness: Offers some of the lowest fees in the industry with additional BNB token discounts and high-volume tier benefits.
Bybit Trading Specialization
Bybit excels in derivatives trading with advanced features for professional traders.
Derivatives Focus: Industry-leading perpetual futures and options trading with up to 100x leverage and sophisticated risk management tools.
Copy Trading Excellence: Over 800,000 master traders with advanced social trading features and performance transparency.
User Experience: Intuitive interface design makes complex derivatives trading accessible to intermediate traders.
OKX Comprehensive Platform
OKX provides balanced feature coverage with strong Web3 integration and competitive pricing.
Trading Variety: Comprehensive spot, margin, futures, and options trading across 400+ cryptocurrencies with competitive fee structures.
Web3 Integration: Unique combination of centralized trading features with decentralized finance access through integrated wallet services.
Innovation Focus: Regular introduction of new trading features and tools, maintaining competitive advantage in evolving markets.
Kraken Security and Compliance
Kraken emphasizes regulatory compliance and security while providing professional trading features.
Regulatory Standing: Strong compliance record and regulatory licenses provide confidence for institutional and security-conscious retail traders.
Professional Tools: Kraken Pro offers advanced trading features with institutional-grade infrastructure and transparent pricing.
Security Focus: Industry-leading security measures and transparent operational practices build user trust and platform reliability.
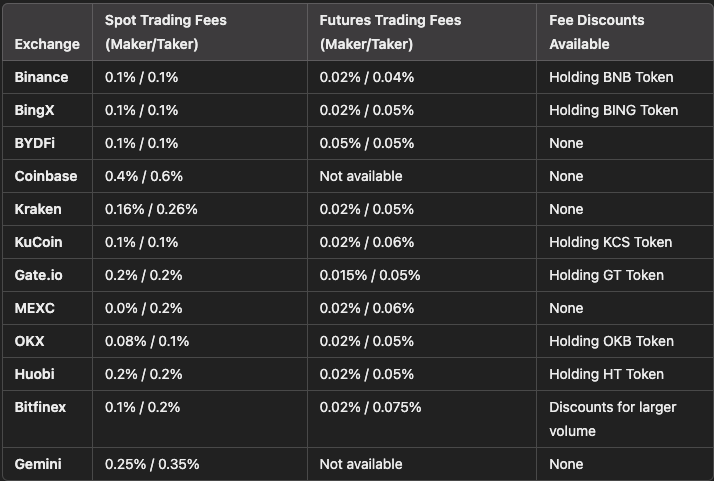
Regional Considerations and Regulations
Trading feature availability varies significantly by jurisdiction due to evolving regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements.
Regulatory Impact on Features
Different regions impose varying restrictions on trading features, affecting platform availability and functionality.
Derivatives Restrictions: Many jurisdictions restrict or prohibit high-leverage derivatives trading for retail customers, limiting futures and margin access.
Licensing Requirements: Exchanges must obtain appropriate licenses to offer specific trading features in regulated markets, affecting service availability.
Consumer Protection: Regulatory bodies often impose leverage limits, risk warnings, and cooling-off periods to protect retail investors.
Geographic Availability
Major exchanges adapt their feature sets based on regional regulatory requirements and market conditions.
US Market Restrictions: American traders face significant limitations on leverage and derivatives products, with separate platforms often required.
European Compliance: MiCA regulations and national laws create varying feature availability across European Union member states.
Asian Market Diversity: Different Asian countries have vastly different regulatory approaches, from restrictive to highly permissive trading environments.
Getting Started with Exchange Trading Features
New traders should approach advanced trading features systematically, starting with basic spot trading before progressing to more complex instruments.
Beginner Trading Path
A structured approach to learning trading features reduces risk while building necessary skills and experience.
Spot Trading Mastery: Begin with simple buy-and-hold strategies using small amounts to understand market dynamics and exchange interfaces.
Paper Trading Practice: Use demo accounts or small amounts to practice advanced features without significant financial risk.
Educational Resources: Utilize exchange-provided educational materials, webinars, and tutorials before attempting complex strategies.
Progressive Feature Adoption
Gradual introduction of advanced features allows traders to build competence while managing risk appropriately.
Low-Leverage Margin: Start with 2x-3x leverage on margin trades to understand borrowing mechanics and liquidation risks.
Basic Derivatives: Begin with simple perpetual futures before progressing to options and complex multi-leg strategies.
Risk Management Priority: Implement stop-losses, position sizing, and other risk controls before increasing trade complexity or size.
Platform Selection Criteria
Choose exchanges based on specific feature requirements, regulatory compliance, and risk tolerance.
Feature Requirements: Match exchange capabilities with intended trading strategies and required features for optimal platform selection.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure chosen exchanges operate legally in your jurisdiction and provide appropriate user protections.
Security Standards: Prioritize exchanges with strong security records, insurance coverage, and transparent operational practices.
Future Evolution of Trading Features
The cryptocurrency trading landscape continues evolving rapidly, with new features and improvements regularly introduced across major platforms.
Technology Innovations
Advancing technology enables more sophisticated trading features and improved user experiences.
AI and Machine Learning: Automated market making, intelligent order routing, and predictive analytics enhance trading efficiency and profitability.
Cross-Chain Integration: Multi-blockchain support and cross-chain derivatives enable trading across diverse cryptocurrency ecosystems.
Institutional Tools: Professional-grade features like prime brokerage, OTC trading, and custody integration cater to institutional adoption.
Regulatory Evolution
Changing regulatory frameworks will continue shaping available trading features and market structure.
Standardization Efforts: Global regulatory coordination may lead to more consistent feature availability across jurisdictions.
Consumer Protection Enhancement: Additional safeguards and risk management tools will likely become mandatory for retail trading platforms.
Institutional Framework Development: Clearer institutional trading regulations may enable broader professional market participation.
Conclusion
Trading features on cryptocurrency exchanges have evolved into sophisticated ecosystems providing comprehensive tools for traders across all experience levels and strategy preferences. The combination of spot trading, margin trading, futures contracts, options, and advanced order management creates opportunities for both conservative investors and aggressive speculators.
Understanding these features, their benefits, risks, and appropriate applications is essential for successful cryptocurrency trading. While basic spot trading remains the foundation for most traders, advanced features like margin and derivatives trading can enhance portfolio performance when used appropriately with proper risk management.
The continuing evolution of exchange trading features, driven by technological advancement and regulatory development, promises even more sophisticated tools and opportunities for cryptocurrency market participants. Success in this environment requires continuous learning, careful risk management, and strategic feature utilization aligned with individual goals and risk tolerance.
Ready to explore advanced trading features? Learn more about choosing the right platform in our complete crypto exchange guide and discover which exchanges offer the trading features that match your strategy and risk profile.
Risk Warning: Advanced trading features like margin, futures, and options involve significant risk and may not be suitable for all investors. High leverage can result in substantial losses exceeding initial investments. Please trade responsibly and consider your risk tolerance before using advanced features.
