Complete Futures Trading Guide for Beginners in 2025
Updated on August 31, 2025 • Reading time: 14–18 minutes
Risk Notice: Crypto futures are high-risk derivatives. Only trade what you can afford to lose. Nothing in this article is financial advice.
What Is Futures Trading in Crypto?
Crypto futures are derivative contracts that track an underlying asset’s price (e.g., BTC, ETH) and let you take long (bet price up) or short (bet price down) positions without owning the asset directly. Two major types exist: perpetual futures (no expiry) and dated futures (with expiry).
Compared with spot trading, futures introduce leverage, funding payments (for perpetuals), and liquidation mechanics. The appeal: capital efficiency and two-way opportunities; the cost: tighter risk management and discipline.
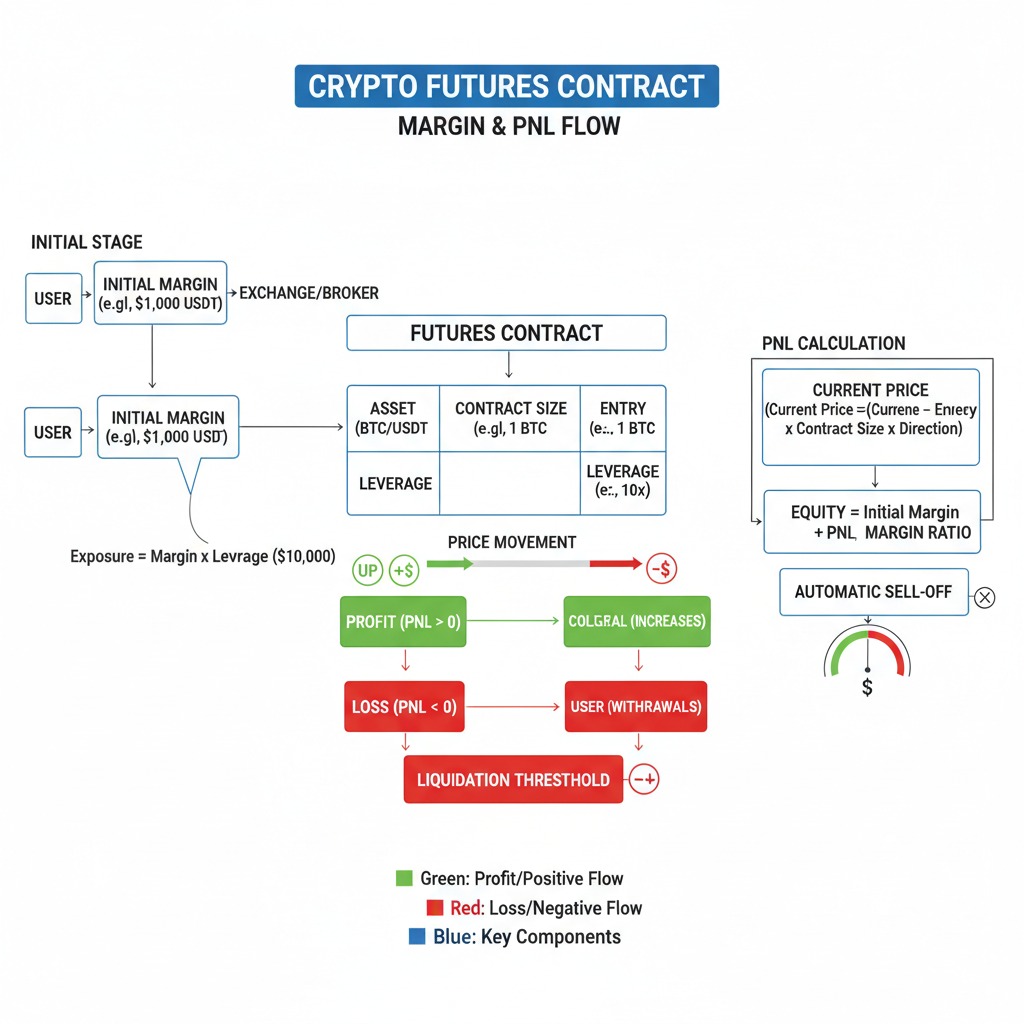
How Crypto Futures Work
Long and Short
You profit on a long when price rises and on a short when price falls. PnL is calculated on contract size, entry/exit prices, and notional exposure.
Leverage and Margin
Leverage multiplies exposure relative to your margin. Higher leverage reduces margin requirements but increases liquidation risk. Use conservative levels and position sizing aligned with your risk tolerance.
Perpetual Futures and Funding
Perpetuals use a funding rate—periodic payments between longs and shorts—to anchor contract price near the spot index. Positive funding means longs pay shorts; negative funding means shorts pay longs.
Liquidation Mechanics
When your margin falls below maintenance requirements, positions can be liquidated. Avoid this via proper sizing, timely stop-losses, and avoiding excessive leverage.
Pros and Cons
Pros
- Two-way opportunities: Long or short trending markets.
- Capital efficiency: Leverage allows smaller capital to control larger exposure.
- Hedging: Offset risk on spot holdings with a futures hedge.
Cons
- Higher risk: Liquidation risk rises with leverage.
- Funding costs: Perpetuals may incur funding payments that erode returns.
- Discipline intensive: Requires rigorous risk management and emotional control.
Best Exchanges for Futures Trading
Choose exchanges with deep liquidity, robust risk engines, clear fee schedules, and strong security. Explore detailed platform insights here:
- Binance Exchange Review — Open an account: Binance (ref)
- Bybit Exchange Features — Join: Bybit (ref)
- OKX Exchange Benefits — Join: OKX (ref)
- KuCoin — Join: KuCoin (ref)
- Gate.io — Join: Gate.io (ref)
- MEXC — Join: MEXC (ref)
- Bitget — Join: Bitget (ref)
- BingX — Join: BingX (ref)
- WhiteBIT — Join: WhiteBIT (ref)
Also see the cluster overview: Trading Features on Exchanges and related: Spot Trading, Coinbase Exchange Explained.
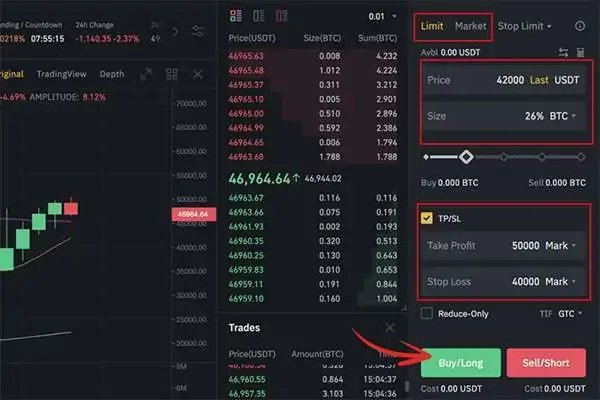
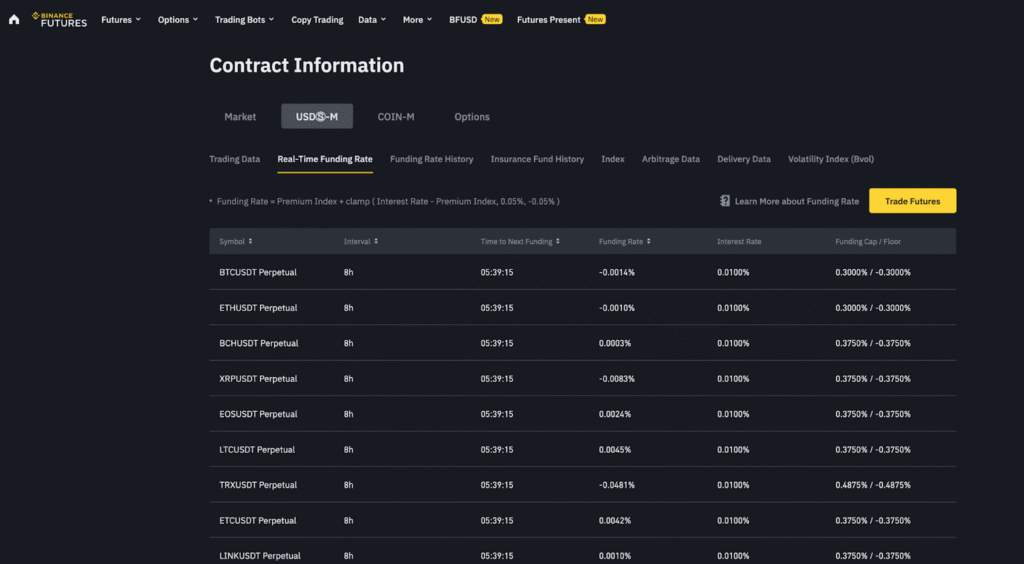
Fees and True Trading Costs
Total futures costs typically include: maker/taker trading fees, funding payments (perpetuals), and withdrawal network fees. Costs vary by exchange, product, and VIP tier. Always review the official fee page before trading.
| Exchange | Products | Trading Fees (range) | Funding (perpetuals) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | Perpetuals, Quarterly | Varies by tier | Long ↔ Short (periodic) | High liquidity; multiple margin modes |
| Bybit | USDT/USDC Perpetuals | Varies by tier | Long ↔ Short (periodic) | Advanced order types; portfolio margin |
| OKX | Perpetuals, Futures | Varies by tier | Long ↔ Short (periodic) | Robust risk engine; options ecosystem |
Tip: Track funding over time; frequent positive funding can reduce long profitability, while negative funding can reduce short profitability. If unsure, reduce size or step aside.
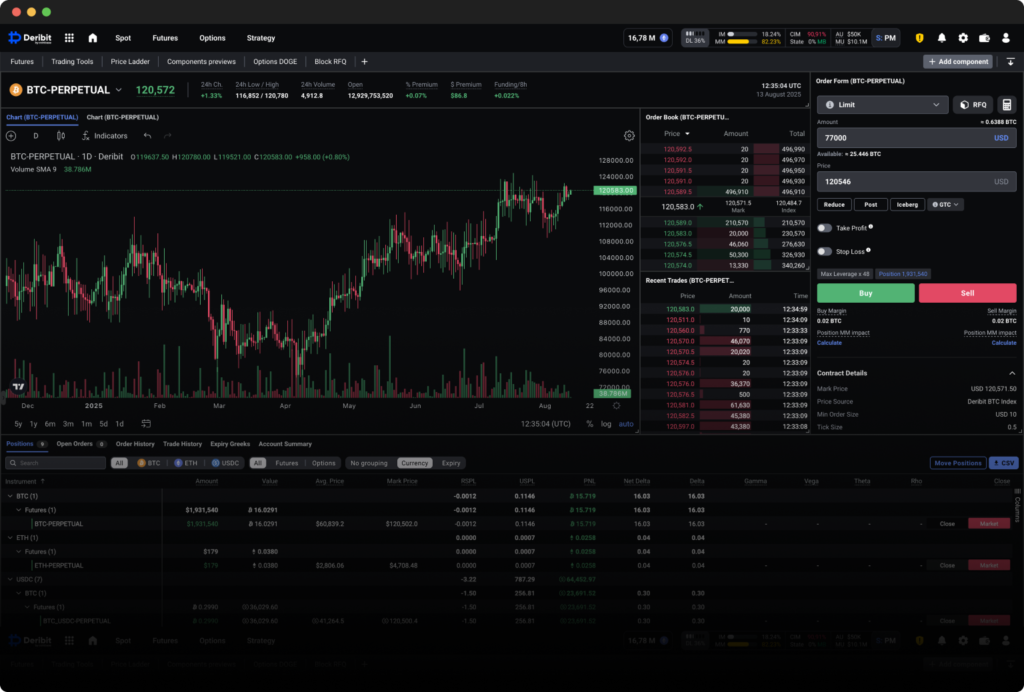
Core Strategies (With Risk Controls)
Position Sizing Formula
Define risk per trade as a percentage of equity (e.g., 0.5%–1%).
Position Size (contracts) = (Equity × %Risk) / (Entry − Invalidation)Adjust for contract multiplier and tick value as needed. Always place a stop-loss at the invalidation level.
Scalping / Day Trading
- Focus on liquid pairs and sessions with strong volume.
- Use predefined setups (e.g., breakout + retest) and fixed RR (e.g., 1:1.5+).
- Avoid overtrading; cap daily loss and number of trades.
Swing Trading
- Define trend bias (HTF structure) then refine on LTF for entries.
- Trail stops as structure develops; avoid adding to losers.
- Mind funding impacts on multi-day holds.
Hedging
- Offset spot exposure by shorting correlated perpetuals during drawdowns.
- Size hedge based on beta and desired protection (partial vs. full).
- Lift hedges tactically to restore upside when conditions improve.
Risk Guardrails
- Leverage conservatively; prefer isolated margin until consistent.
- Use hard stops; never widen stops after entry.
- Respect max daily loss; stop trading after hitting it.
Common Risks and Mistakes
- Over-leverage: Small fluctuations can trigger liquidation.
- No invalidation: Entries without a clear stop invite large losses.
- Ignoring funding: Costs compound on longer holds.
- Revenge trading: Emotional decisions worsen drawdowns.
- Position correlation: Multiple longs on correlated alts = hidden concentration.
Security and Regulation
Prefer exchanges with strong custody, risk controls, and transparent policies. Check regional availability and compliance before trading derivatives.
- Account protections: 2FA, anti-phishing codes, withdrawal allowlists.
- Operational safeguards: cold storage practices, monitoring, incident response.
- Regulatory scope: futures access varies by jurisdiction; verify your region’s rules before trading.
Explore more: Trading Features on Exchanges, Binance Review, OKX Benefits, Bybit Features.
Getting Started: A Safe Path
- Open and secure your account on a reputable exchange (2FA, security codes, allowlists).
- Complete KYC and fund your account with stablecoins for margin.
- Practice on testnet or small size with isolated margin and hard stops.
- Define your plan: setups, invalidation, risk %, max daily loss.
- Journal entries/exits, reasoning, and emotions. Iterate weekly.
Quick access:
- Binance (ref): Start on Binance
- Bybit (ref): Start on Bybit
- OKX (ref): Start on OKX
Futures vs. Spot, Margin, Copy Trading
| Feature | Futures | Spot | Margin | Copy Trading |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership of Asset | No (derivative) | Yes | Yes (borrowed funds) | Varies (follows leader) |
| Leverage | Yes | No | Yes | Indirect |
| Funding Payments | Perpetuals only | None | Interest on borrow | N/A |
| Liquidation Risk | High (manage strictly) | None | Moderate | Depends on strategy |
For basics, see Spot Trading. For exchange-level view, see Trading Features on Exchanges.
2025 Outlook
- Richer risk tools: portfolio margin, cross-collateral, and smarter liquidation buffers.
- More automation: rules-based bots for entries, exits, and journal prompts.
- Compliance-first access: clearer, region-specific derivative availability and disclosures.
FAQs
Is Crypto Futures Trading Safe for Beginners?
Short answer: It is high risk and not inherently “safe.” Beginners should start tiny, use isolated margin, and always place stop-losses.
How Much Leverage Should I Use?
Principle: Use the minimum leverage needed to express your edge. Many profitable traders use conservative leverage and focus on sizing and invalidation.
Which Exchange Is Best for Futures?
Choose deep liquidity, robust risk engine, clear fees, and strong security. Consider Binance, Bybit, and OKX.
Can I Lose More Than I Deposit?
Liquidations happen when margin is insufficient. Manage risk so that single trades cannot wipe out your account. Avoid excessive leverage.
What Is Funding Rate and Why Does It Matter?
Funding is a periodic payment between longs and shorts in perpetuals. It can erode returns if you hold during unfavorable cycles—monitor it before holding positions for long.
