Crypto Futures Fees & Funding Comparison 2025: Complete Cost Analysis Guide
Introduction: Why Fees Matter More Than You Think
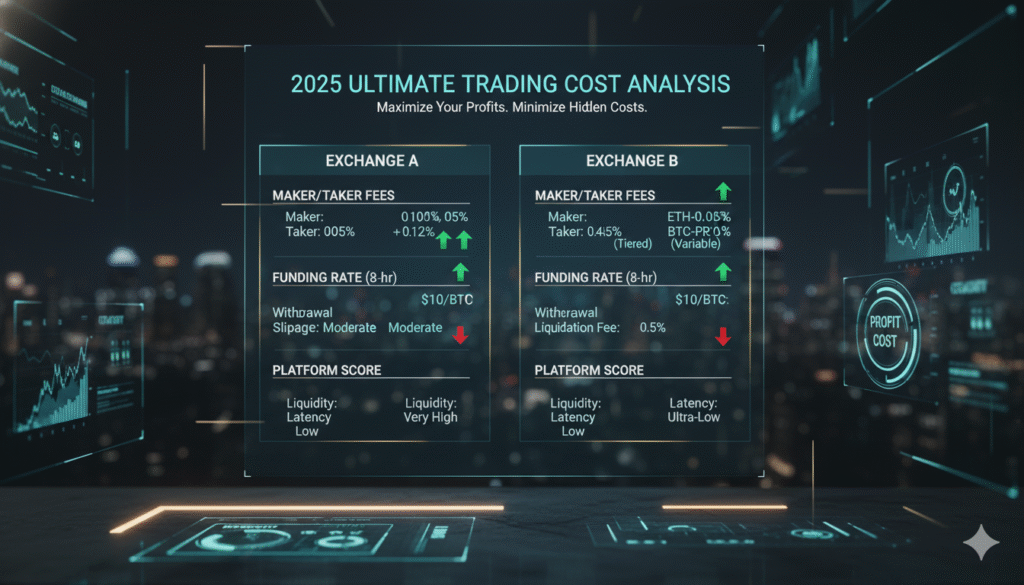
Understanding crypto futures fees and funding comparison is critical for any trader serious about maximizing profitability. While most traders focus exclusively on market analysis and entry points, trading costs can silently erode 15-30% of potential gains over time. A seemingly small difference of 0.02% in maker fees can translate to thousands of dollars in savings for active traders.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dissect every fee component across major cryptocurrency exchanges—from maker/taker fees and funding rates to withdrawal costs and liquidation charges. Whether you’re executing scalping strategies with dozens of daily trades or holding leveraged positions for weeks, understanding these costs will directly impact your bottom line.
Bottom line: The right exchange selection based on your trading style and volume can save you thousands annually. This guide provides the data-driven comparison you need to make that informed decision.
Understanding the Complete Fee Structure
Before comparing specific exchanges, it’s essential to understand the complete ecosystem of fees in crypto futures trading. Unlike spot trading, futures contracts involve multiple cost layers that accumulate throughout your trading journey.
The Four Primary Fee Categories
1. Trading Fees (Maker/Taker)
Trading fees represent the most visible cost component and are charged on every order execution. These fees split into two distinct types:
Maker Fees: Applied when you add liquidity to the order book by placing limit orders that don’t immediately execute. These orders “make” the market by providing depth.
Taker Fees: Charged when you remove liquidity by executing market orders or limit orders that immediately match existing orders in the book.
Most exchanges implement tiered fee structures where costs decrease as your 30-day trading volume increases. Some platforms even offer negative maker fees (rebates) for high-volume traders, effectively paying you to provide liquidity.
2. Funding Rates
Funding rates constitute the most misunderstood yet potentially costly element of perpetual futures trading. These periodic payments balance the perpetual contract price with the underlying spot price.
How Funding Rates Work:
- Positive Funding Rate: When futures trade at a premium to spot, long position holders pay shorts every 8 hours
- Negative Funding Rate: When futures trade at a discount, short position holders pay longs
- Typical Range: -0.05% to +0.05%, though extreme market conditions can push rates above 1%
Funding rates aren’t fees paid to exchanges—they’re transfers between traders. However, consistently paying funding over extended periods significantly impacts profitability.
3. Withdrawal and Deposit Fees
Deposit Fees: Most exchanges offer free cryptocurrency deposits, though fiat deposits via credit cards or bank transfers often incur 2-5% charges.
Withdrawal Fees: Cryptocurrency withdrawals typically include network transaction fees, which vary dramatically by blockchain. Bitcoin withdrawals might cost 0.0005 BTC ($12-15 at current prices), while Ethereum withdrawals can range from $5-50 depending on network congestion.
4. Liquidation Fees
When leveraged positions move against you and losses exceed available margin, exchanges automatically liquidate your position to protect their capital. Liquidation fees typically range from 0.05% to 0.5% of the position value and are deducted from remaining margin.
Understanding these fee structures helps you optimize trading strategies. For comprehensive platform comparisons, explore our guide on best crypto exchange platforms.
Major Exchange Fee Comparison: Detailed Breakdown
Let’s examine how leading cryptocurrency exchanges structure their futures trading fees. This comparison focuses on standard account holders before VIP tier discounts.
Binance Futures Fees
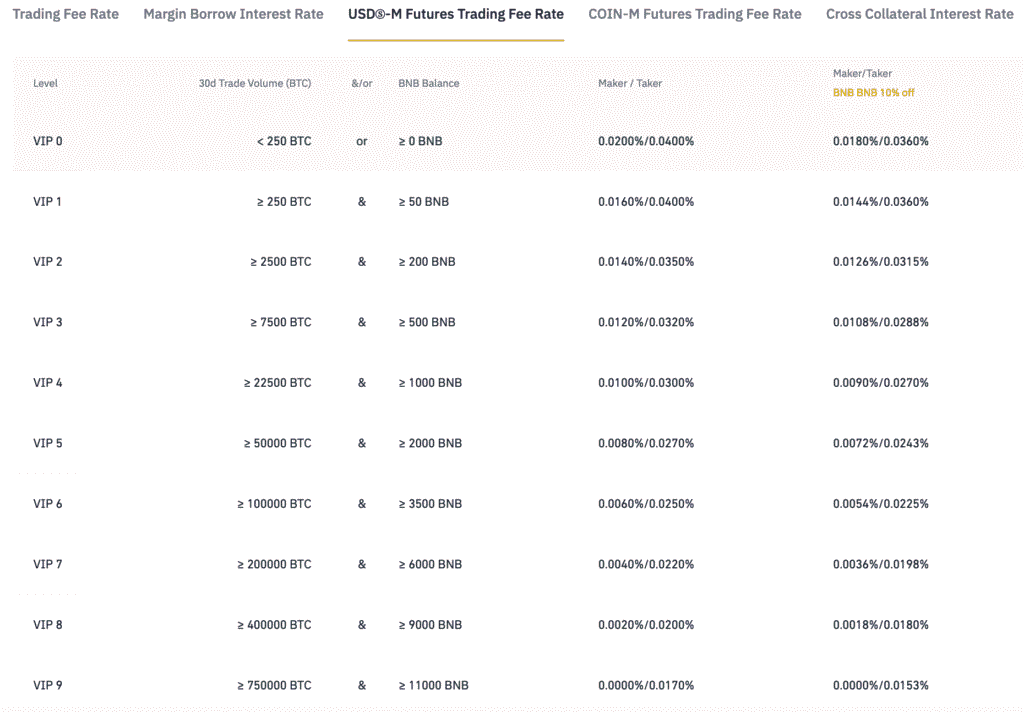
Exchange Overview: As the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange by volume, Binance offers exceptional liquidity and competitive pricing.
Fee Structure:
- Maker Fee: 0.02%
- Taker Fee: 0.04%
- Funding Rate: Every 8 hours, market-dependent (typically -0.01% to +0.01%)
- Withdrawal Fees: Vary by cryptocurrency (BTC: ~0.0005 BTC)
- Deposit Fees: Free for crypto; fiat deposits vary by payment method
VIP Tiers: Volume-based discounts reduce fees to as low as 0.012% maker and 0.024% taker for the highest tiers.
Best For: High-volume traders seeking deep liquidity and the broadest cryptocurrency selection.
Sign Up: Join Binance to access competitive futures trading.
Bybit Futures Fees
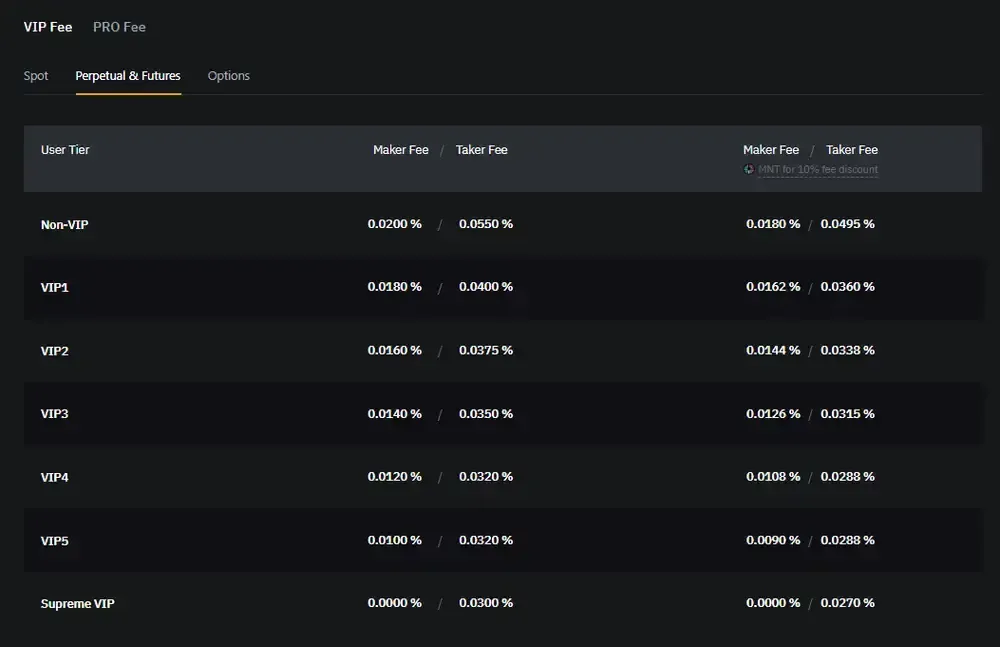
Exchange Overview: Bybit has built a strong reputation as a derivatives-focused platform with institutional-grade infrastructure.
Fee Structure:
- Maker Fee: 0.01%
- Taker Fee: 0.06%
- Funding Rate: Every 8 hours (bi-hourly settlement)
- Withdrawal Fees: Competitive; vary by asset
- Deposit Fees: Free for all cryptocurrencies
Unique Feature: Bybit offers negative maker fees for high-volume traders, meaning you earn rebates for providing liquidity rather than paying fees.
Best For: Professional traders prioritizing maker rebates and advanced charting tools.
Sign Up: Join Bybit for premium derivatives trading.
OKX Futures Fees
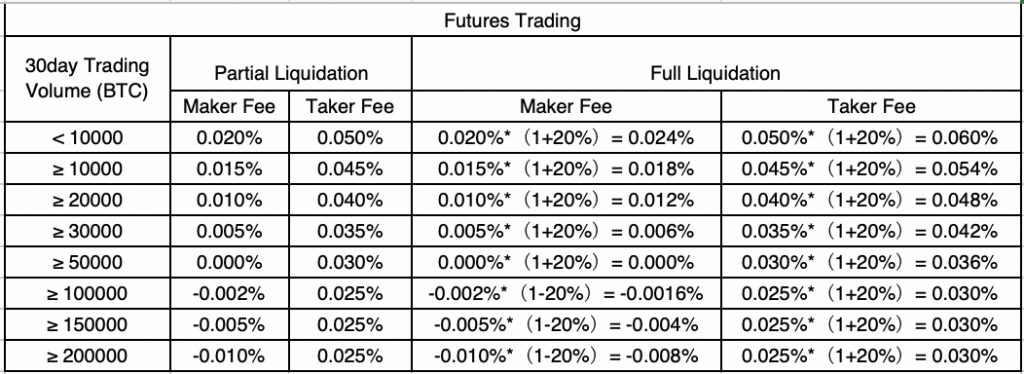
Exchange Overview: OKX delivers a comprehensive trading ecosystem with robust derivatives offerings and global reach.
Fee Structure:
- Maker Fee: 0.02%
- Taker Fee: 0.05%
- Funding Rate: Every 8 hours, algorithmically calculated
- Withdrawal Fees: Asset-dependent, generally competitive
- Deposit Fees: Free for cryptocurrency
VIP Benefits: Tiered structure offers significant discounts for volume traders.
Best For: Traders seeking balance between low fees and extensive altcoin futures selection.
For detailed OKX insights, see our OKX affiliate program analysis.
BingX Futures Fees
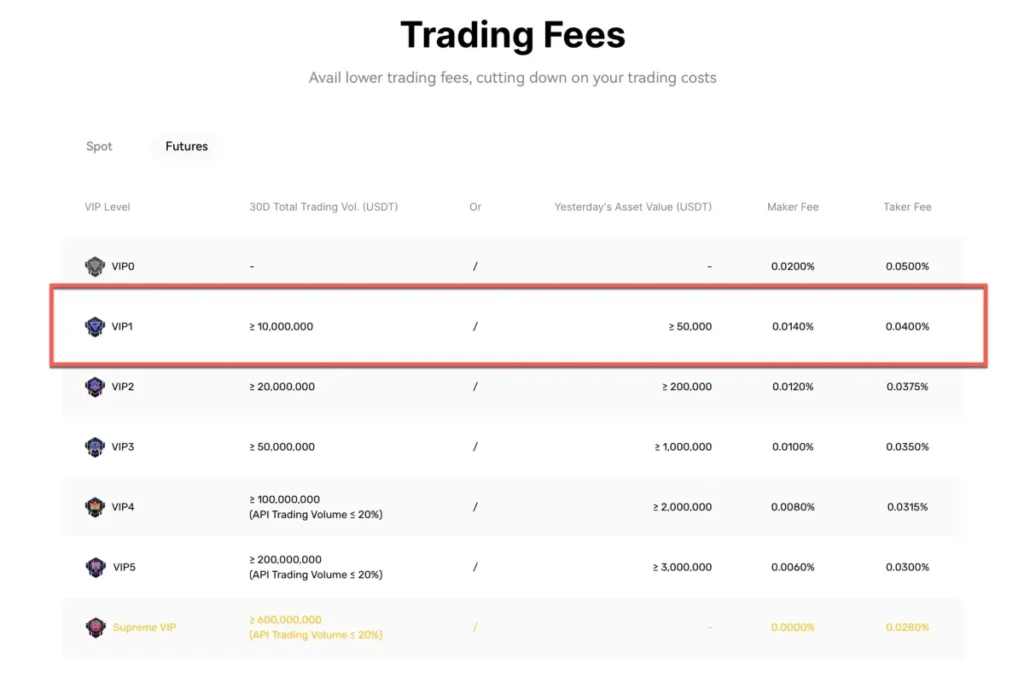
Exchange Overview: BingX distinguishes itself through industry-leading copy trading features alongside competitive futures pricing.
Fee Structure:
- Maker Fee: 0.02%
- Taker Fee: 0.04%
- Funding Rate: Every 8 hours, typically in line with major exchanges
- Withdrawal Fees: Vary by cryptocurrency; occasional promotional periods with reduced fees
- Deposit Fees: Free for crypto deposits
Unique Advantage: While fees are competitive, BingX’s primary value proposition lies in its copy trading ecosystem with 17,000+ professional traders.
Best For: Traders interested in social trading features combined with standard futures offerings.
Sign Up: Join BingX to explore copy trading opportunities.
MEXC Futures Fees
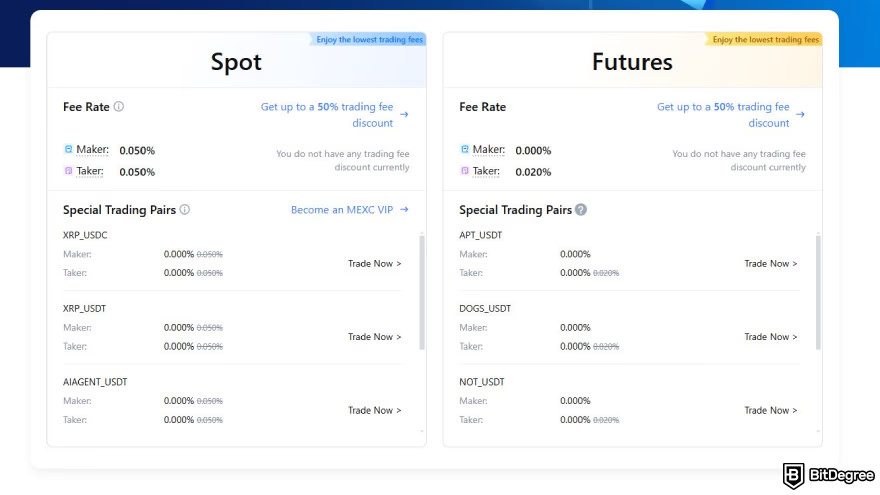
Exchange Overview: MEXC has emerged as a cost-effective alternative with impressive altcoin coverage.
Fee Structure:
- Maker Fee: 0.00% (zero maker fees!)
- Taker Fee: 0.05%
- Funding Rate: Every 8 hours, market-dependent
- Withdrawal Fees: Cryptocurrency-specific, generally reasonable
- Deposit Fees: Free for crypto; various fiat options
Standout Feature: MEXC’s zero maker fees make it exceptionally attractive for limit order traders and market makers.
Best For: Cost-conscious traders focusing on altcoin futures with limit orders.
Sign Up: Join MEXC for zero maker fee trading.
Bitget Futures Fees
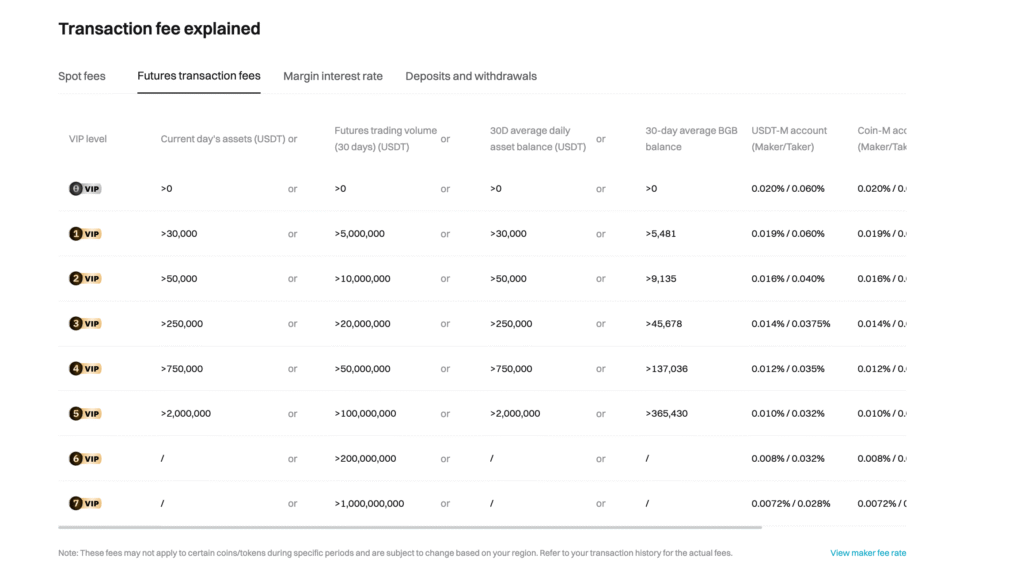
Exchange Overview: Bitget has gained traction through competitive pricing and innovative copy trading features.
Fee Structure:
- Maker Fee: 0.02%
- Taker Fee: 0.06%
- Funding Rate: Every 8 hours
- Withdrawal Fees: Asset-dependent
- Deposit Fees: Free for cryptocurrency
Notable Feature: Strong copy trading community similar to BingX, with competitive fee structure.
Best For: Traders seeking alternatives to major exchanges with solid copy trading infrastructure.
Funding Rates: The Hidden Cost of Perpetual Futures
Funding rates deserve special attention as they represent ongoing costs that many traders underestimate. Unlike one-time trading fees, funding accumulates every 8 hours for as long as you maintain open positions.
Real-World Funding Rate Impact
Let’s examine a practical scenario:
Trading Scenario:
- Position Size: $10,000 long position in BTC/USDT
- Funding Rate: +0.01% (positive, meaning longs pay shorts)
- Holding Period: 7 days (21 funding periods)
Calculation:
- Cost per funding period: $10,000 × 0.01% = $1
- Total 7-day cost: $1 × 21 = $21
- Annualized impact: Approximately 10.95% of position value
This example uses a relatively modest funding rate. During extreme bull markets, funding rates can spike to 0.1% or higher, dramatically increasing costs.
Funding Rate Optimization Strategies
1. Monitor Funding Schedules: Most exchanges charge funding at fixed 8-hour intervals (00:00, 08:00, 16:00 UTC). Consider closing positions before high funding periods and reopening afterward.
2. Cross-Exchange Arbitrage: When funding rates diverge significantly between exchanges, sophisticated traders execute opposing positions to collect positive funding while hedging price risk.
3. Choose Lower-Funding Assets: Different cryptocurrencies exhibit different funding rate behaviors. Research historical funding patterns before position entry.
4. Time Your Entries: Avoid entering leveraged positions immediately before funding collection, particularly during periods of elevated rates.
For traders interested in understanding broader market dynamics, explore our crypto trading for beginners guide.
Withdrawal Fee Comparison: The Exit Cost
While trading fees capture most attention, withdrawal costs significantly impact profitability, especially for traders who frequently move funds between exchanges or to cold storage.
Blockchain-Specific Withdrawal Costs
Bitcoin (BTC):
- Binance: 0.0005 BTC (~$12.50)
- Bybit: 0.0005 BTC (~$12.50)
- OKX: 0.0004 BTC (~$10.00)
- BingX: 0.0005 BTC (~$12.50)
Ethereum (ETH):
- Binance: 0.005 ETH (~$10.00)
- Bybit: 0.005 ETH (~$10.00)
- OKX: 0.005 ETH (~$10.00)
- BingX: 0.006 ETH (~$12.00)
USDT (ERC-20):
- Binance: 25 USDT
- Bybit: 25 USDT
- OKX: 20 USDT
- BingX: 25 USDT
Optimization Tip: Choose blockchain networks strategically. Withdrawing USDT via TRC-20 (Tron) typically costs only 1 USDT compared to 25 USDT via ERC-20 (Ethereum).
VIP Tier Programs: Volume-Based Discounts
All major exchanges implement VIP tier systems that reward high-volume traders with progressively lower fees. Understanding these structures helps optimize costs for active traders.
Volume Requirements Comparison
Binance VIP Structure:
- VIP 1: $10M+ 30-day volume → 0.018% maker / 0.036% taker
- VIP 9: $150B+ 30-day volume → 0.012% maker / 0.024% taker
Bybit VIP Structure:
- VIP 1: $10M+ 30-day volume → 0.006% maker / 0.050% taker
- VIP Pro: $3B+ 30-day volume → -0.010% maker / 0.030% taker (maker rebate!)
OKX VIP Structure:
- VIP 1: $5M+ 30-day volume → 0.015% maker / 0.040% taker
- VIP 5: $500M+ 30-day volume → 0.010% maker / 0.030% taker
Strategic Consideration: If your monthly trading volume approaches VIP thresholds, concentrating activity on one platform maximizes tier benefits rather than fragmenting volume across multiple exchanges.
Fee Impact by Trading Style
Different trading strategies experience varying fee impacts. Understanding your style helps optimize exchange selection.
Scalping (High-Frequency Trading)
Characteristics: 10-100+ trades daily; positions held seconds to minutes.
Primary Cost Factors:
- Trading fees dominate (funding rates minimal due to short holding periods)
- Every 0.01% fee reduction significantly impacts profitability
- Maker rebates highly valuable
Optimal Exchanges:
- MEXC (zero maker fees)
- Bybit (maker rebates for high volume)
- Binance (deep liquidity minimizes slippage)
Day Trading
Characteristics: 5-20 trades daily; positions held minutes to hours.
Primary Cost Factors:
- Trading fees primary concern
- Occasional funding charges if holding past 8-hour intervals
- Withdrawal fees less relevant
Optimal Exchanges:
- Bybit (low maker fees)
- OKX (balanced fee structure)
- Binance (liquidity and reliability)
Swing Trading
Characteristics: 1-5 trades weekly; positions held days to weeks.
Primary Cost Factors:
- Funding rates become significant
- Trading fees less impactful
- Withdrawal fees matter for position management
Optimal Exchanges:
- Binance (competitive funding rates)
- OKX (stable funding mechanisms)
- Bybit (reliable funding calculations)
Position Trading (Long-Term Holdings)
Characteristics: Several trades monthly; positions held weeks to months.
Primary Cost Factors:
- Funding rates dominate cost structure
- Must actively monitor and manage funding exposure
- Consider spot holdings instead for very long-term positions
Optimal Exchanges:
- Consider whether futures are appropriate
- If leveraged exposure necessary: Binance or OKX for stable funding
For those new to different trading approaches, review our introduction to crypto trading guide.
Hidden Fees and Costs to Watch
Beyond standard fee schedules, several hidden costs can impact profitability:
Slippage
Slippage occurs when market orders execute at worse prices than expected due to insufficient liquidity. While not a direct fee, slippage represents real cost.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Trade high-liquidity pairs on high-liquidity exchanges
- Use limit orders instead of market orders when possible
- Avoid trading during low-volume periods
Conversion Fees
Converting between cryptocurrencies often incurs trading fees even if not explicitly labeled as “conversion fees.”
Example: Converting USDT to BTC to ETH involves two trading fee instances.
Interest on Borrowed Funds (Margin)
Some exchanges charge daily or hourly interest on margin borrowed for leveraged positions, separate from funding rates.
Typical Rates: 0.01% to 0.1% daily, varying by asset and market conditions.
Premium/Discount on Fiat Purchases
Buying cryptocurrency with fiat currency often includes hidden premiums embedded in exchange rates, effectively adding 1-3% to purchase costs.
Tax Implications of Trading Fees
Trading fees carry important tax implications that vary by jurisdiction:
Fee Deductibility
In many jurisdictions, trading fees are tax-deductible as cost basis adjustments:
Example:
- Buy 1 BTC at $25,000 + $25 fee = $25,025 cost basis
- Sell 1 BTC at $30,000 – $30 fee = $29,970 proceeds
- Taxable gain: $29,970 – $25,025 = $4,945
Record Keeping
Maintain detailed records of all fees paid:
- Trading fees
- Withdrawal fees
- Funding payments/receipts
- Conversion fees
Most exchanges provide fee reports, though cryptocurrency tax software like Koinly or CoinTracker automate this process.
Important: Consult tax professionals familiar with cryptocurrency regulations in your jurisdiction for personalized guidance.
Fee Optimization Checklist
Use this checklist to minimize trading costs:
✓ Exchange Selection
- Compare fees across multiple platforms
- Consider VIP tier eligibility based on volume
- Factor withdrawal fees into total cost analysis
✓ Order Type Strategy
- Use limit orders (maker fees) when time allows
- Reserve market orders (taker fees) for urgent executions
- Set appropriate limit prices to ensure execution
✓ Funding Rate Management
- Monitor funding rates before opening positions
- Consider timing entries/exits around funding periods
- Use funding rate arbitrage during extreme conditions
✓ Withdrawal Optimization
- Batch withdrawals to minimize per-transaction costs
- Choose low-cost blockchain networks (TRC-20 vs ERC-20)
- Time withdrawals during low network congestion
✓ Volume Consolidation
- Concentrate trading on one platform to achieve VIP tiers
- Calculate whether tier benefits justify volume concentration
- Review tier status monthly and adjust strategy
✓ Alternative Cost Reduction
- Use exchange tokens (BNB, OKB) for fee discounts where applicable
- Participate in exchange promotions and fee waivers
- Consider maker rebate programs for high-frequency strategies
Future of Futures Trading Fees
The competitive landscape continues evolving, with several trends shaping future fee structures:
Race to Zero
Exchanges increasingly compete on fees, with several platforms already offering zero maker fees. This trend likely continues as exchanges seek market share through cost advantages.
Token-Based Fee Discounts
Native exchange tokens (BNB, OKB, BGB) provide additional fee discounts, creating ecosystems that reward platform loyalty.
Institutional Fee Structures
As institutional adoption grows, exchanges develop customized fee arrangements for high-volume entities, potentially widening the gap between retail and institutional costs.
Regulatory Impact
Increased regulatory scrutiny may introduce new compliance costs that exchanges pass to users through adjusted fee structures.
For insights into regulatory developments, explore our crypto regulations guide.
Conclusion: Making the Cost-Optimized Choice
Understanding crypto futures fees and funding comparison empowers you to make data-driven exchange selections that significantly impact long-term profitability. While a 0.02% fee difference might seem trivial, it compounds dramatically over thousands of trades or large position sizes.
Key Takeaways:
- Match Exchange to Trading Style: Scalpers need maker rebates; swing traders must monitor funding rates
- Factor All Costs: Trading fees represent only one component; consider funding, withdrawals, and hidden costs
- Leverage VIP Tiers: High-volume traders should consolidate activity to achieve tier discounts
- Monitor Funding Rates: This often-overlooked cost significantly impacts leveraged position profitability
- Optimize Continuously: Fee structures evolve; regularly reassess your exchange selection
The exchange offering the “lowest fees” varies by your specific trading profile. A scalper prioritizing maker fees finds MEXC most cost-effective, while a swing trader concerned about funding stability might prefer Binance or Bybit.
Action Steps:
- Calculate your approximate monthly trading volume
- Identify your primary trading style (scalping, day trading, swing trading)
- Compare total costs (trading + funding + withdrawal) across top exchanges
- Open accounts on 2-3 platforms to test fee structures with real capital
- Monitor and optimize quarterly as trading patterns evolve
By systematically applying the analysis framework in this guide, you’ll minimize trading costs while maximizing capital efficiency—giving you the competitive edge necessary for consistent profitability in cryptocurrency futures markets.
Ready to start trading with optimized costs? Explore our recommended exchanges:
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency futures trading involves substantial risk of loss and is not suitable for all investors. Leverage amplifies both gains and losses. This guide is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Always conduct independent research and only invest capital you can afford to lose.
