Crypto Exchange Security Guide 2025: Regulations & Safety Measures
Crypto exchange security determines whether your digital assets remain protected or become another victim of the $4 billion in cryptocurrency stolen annually. Understanding security measures, regulatory compliance, and personal protection strategies helps you navigate the cryptocurrency ecosystem safely while maximizing investment returns.
Exchange security encompasses platform infrastructure protection, regulatory compliance frameworks, and user asset safeguarding measures. Leading platforms like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken implement enterprise-grade security protocols including cold storage, multi-signature wallets, and comprehensive insurance coverage.
The regulatory landscape continues evolving with new legislation like the GENIUS Act and SEC Crypto Task Force initiatives providing clearer guidelines for crypto exchanges. Professional traders prioritize platforms demonstrating regulatory compliance, transparent operations, and proven security track records when selecting trading venues.
This comprehensive guide analyzes exchange security measures, global regulatory frameworks, compliance requirements, and personal protection strategies. You will learn about cold storage systems, proof of reserves, insurance coverage, and advanced security techniques used by institutional investors to protect cryptocurrency investments.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Crypto Exchange Security
- Major Exchange Security Comparison
- Cold Storage and Hot Wallet Systems
- Regulatory Frameworks Worldwide
- US Cryptocurrency Regulations 2025
- European Union Crypto Compliance
- Asia-Pacific Regional Regulations
- Exchange Insurance and Protection
- Proof of Reserves and Transparency
- Personal Security Best Practices
- Common Security Threats and Prevention
- Regulatory Compliance for Traders
- Future of Crypto Security and Regulation
- FAQs
- Choose Secure Exchanges
Understanding Crypto Exchange Security
Crypto exchange security encompasses multiple layers of protection including infrastructure security, asset custody, regulatory compliance, and user account protection. Modern exchanges implement enterprise-grade security frameworks combining traditional financial industry standards with blockchain-specific safeguards.
Security architecture typically includes cold storage systems holding 90%+ of user funds offline, hot wallets for trading liquidity, multi-signature authorization systems, and real-time monitoring for suspicious activities. Leading exchanges undergo regular security audits and maintain compliance with international standards including SOC 2 Type II and ISO 27001 certifications.
Core security components include:
- Cold storage systems: Offline storage protecting majority of user funds
- Multi-signature wallets: Requiring multiple authorizations for transactions
- Two-factor authentication: Additional verification layers for user accounts
- Real-time monitoring: Automated systems detecting suspicious activities
- Regular security audits: Third-party assessments of security infrastructure
- Employee background checks: Vetting personnel with system access
- Incident response plans: Procedures for handling security breaches
Security vs Convenience Trade-offs
Exchange security measures often create trade-offs between protection and user convenience. Highly secure systems may require additional verification steps, longer withdrawal processing times, and complex authentication procedures that some users find cumbersome.
Common security-convenience considerations:
- Withdrawal limits: Daily/monthly limits balance security with user flexibility
- Verification requirements: KYC procedures increase security but reduce privacy
- Multi-factor authentication: Enhanced security with additional login steps
- Cold storage delays: Withdrawal processing times for maximum security
- Geographic restrictions: Regulatory compliance limiting service availability
Professional traders typically accept security-focused inconveniences in exchange for asset protection, while casual users may prefer platforms balancing security with ease of use. Understanding these trade-offs helps inform platform selection based on individual priorities and risk tolerance.
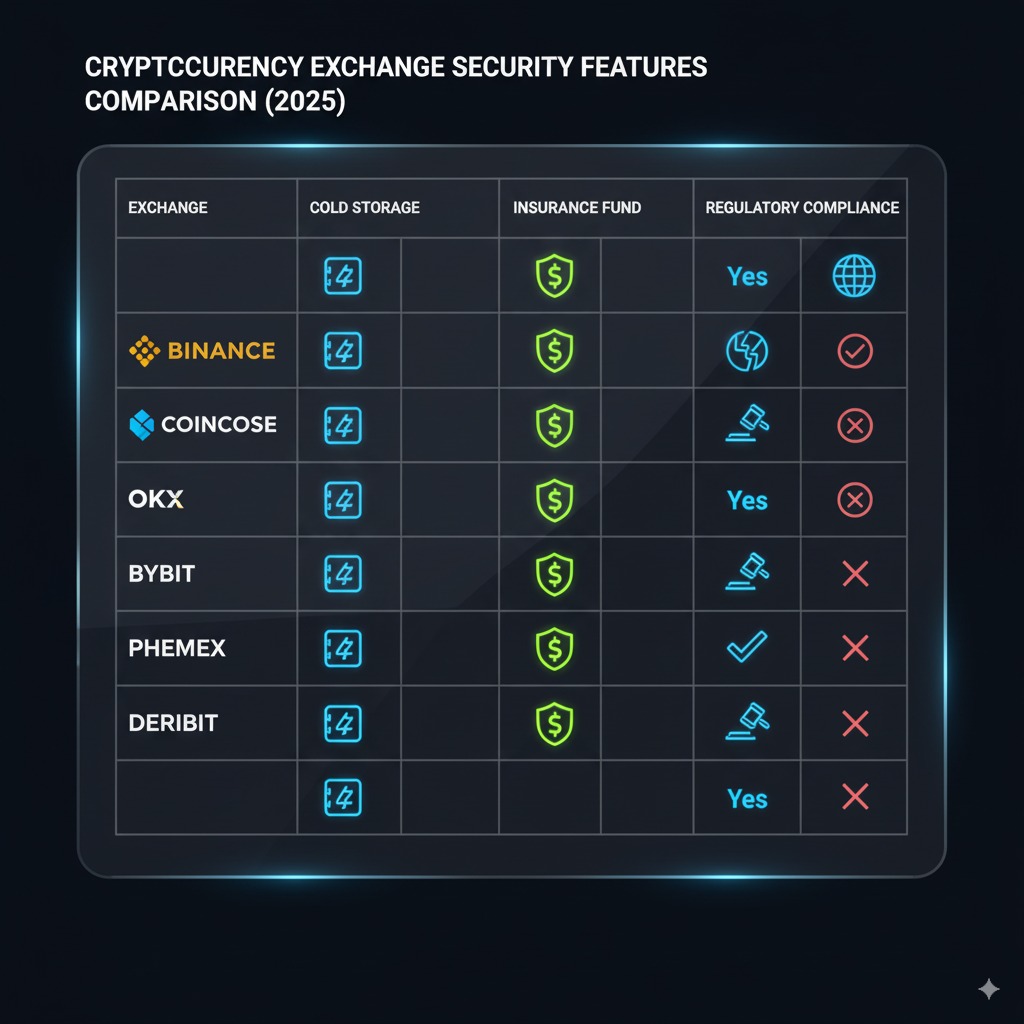
Major Exchange Security Comparison
Binance Security Infrastructure
Binance operates one of the most comprehensive security frameworks in the cryptocurrency industry, protecting over $100 billion in user assets through multi-layered security systems. The platform’s Secure Asset Fund for Users (SAFU) maintains $1+ billion emergency insurance coverage.
Binance security features:
- Cold storage: 95% of user funds stored offline in secure facilities
- SAFU insurance: $1+ billion emergency fund protecting user assets
- Multi-signature wallets: Requiring multiple authorizations for fund movements
- 24/7 monitoring: Real-time security operations center tracking suspicious activities
- Whitelist addresses: Mandatory 24-hour waiting period for new withdrawal addresses
- Anti-phishing codes: Personalized codes in official communications
- Device management: Session monitoring and suspicious device alerts
Advanced security measures:
- Risk management system: Automated algorithms detecting unusual trading patterns
- Proof of reserves: Regular attestations verifying platform solvency
- Bug bounty program: Rewards up to $100,000 for security vulnerability discovery
- Compliance team: 750+ employees dedicated to regulatory and security compliance
- Geographic diversification: Security infrastructure distributed across multiple jurisdictions
Coinbase Security Standards
Coinbase prioritizes institutional-grade security with 98% of customer funds stored offline and comprehensive insurance coverage through Lloyd’s of London. The platform’s security-first approach targets compliance-focused institutional and retail investors.
Coinbase security architecture:
- Cold storage: 98% of customer cryptocurrency stored offline
- Insurance coverage: FDIC protection for USD balances, private insurance for crypto
- Multi-sig technology: Hardware security modules protecting private keys
- Real-time monitoring: Advanced fraud detection and prevention systems
- Employee security: Background checks and security training for all personnel
- Data encryption: AES-256 encryption for sensitive data storage
- Network security: DDoS protection and intrusion detection systems
Regulatory compliance advantages:
- US-regulated platform: Licensed money transmitter in all operating states
- SOC 2 Type II certified: Annual third-party security audits
- ISO 27001 compliance: International information security standards
- Regular penetration testing: External security assessments and vulnerability scanning
- Segregated customer funds: Legal separation of customer and operational assets
Kraken Security Excellence
Kraken maintains an exceptional security record as one of the few major exchanges never experiencing a successful hack resulting in customer fund loss. The platform emphasizes transparency and security-focused operations since 2011.
Kraken security highlights:
- Zero successful hacks: Unblemished security record since platform inception
- Cold storage: Majority of customer funds secured in offline storage
- Multi-factor authentication: Mandatory 2FA with various authentication methods
- Global Pass (2FA): Hardware security key support for maximum account protection
- Encrypted databases: End-to-end encryption for sensitive customer information
- Physical security: Secured data centers with biometric access controls
- Legal compliance: Licensed operations across multiple regulated jurisdictions
Transparency initiatives:
- Proof of reserves: Regular cryptographic proof of customer fund backing
- Open-source security: Selected security tools published for community review
- Security blog: Regular updates on security measures and threat analysis
- Bug bounty program: Community-driven security vulnerability identification
- Regulatory cooperation: Active engagement with global regulatory authorities
Other Major Platform Security
Leading cryptocurrency exchanges implement varying security approaches balancing protection, regulatory compliance, and user experience. Regional platforms often excel in specific security aspects while maintaining competitive feature sets.
Security comparison across platforms:
| Exchange | Cold Storage | Insurance | Hack History | Regulatory Status | Security Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | 95% | $1B+ SAFU | 2019 hack ($40M) | Global licenses | 9.5/10 |
| Coinbase | 98% | FDIC + Private | No major hacks | US regulated | 9.8/10 |
| Kraken | 90%+ | Limited | No hacks | Multi-jurisdiction | 9.7/10 |
| OKX | 95% | Custom fund | No major hacks | Seychelles | 8.5/10 |
| Bybit | 90% | Insurance fund | No major hacks | Dubai/Singapore | 8.0/10 |
Cold Storage and Hot Wallet Systems
Cold Storage Architecture
Cold storage systems keep the majority of cryptocurrency funds completely offline, eliminating internet-based attack vectors while maintaining operational functionality for trading activities. Leading exchanges store 90-98% of customer assets in cold storage facilities with military-grade physical security.

Cold storage implementation methods:
- Hardware security modules: Tamper-resistant devices generating and storing private keys
- Air-gapped systems: Computers never connected to internet networks
- Geographic distribution: Storage facilities across multiple secure locations
- Multi-signature requirements: Multiple key holders required for fund access
- Time-locked transactions: Delayed execution preventing unauthorized transfers
- Physical vault storage: Bank-grade facilities with biometric access controls
Cold storage benefits include:
- Elimination of internet attacks: Offline systems immune to online threats
- Physical security controls: Military-grade facilities protecting hardware
- Multi-party authorization: Distributed key management preventing single points of failure
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting institutional custody requirements
- Insurance eligibility: Enhanced coverage options for properly secured assets
Hot Wallet Operations
Hot wallets maintain smaller cryptocurrency balances connected to internet infrastructure, enabling instant trading execution and withdrawal processing while exposing limited funds to online risks. Exchanges typically hold 2-10% of total assets in hot wallets.
Hot wallet security measures:
- Minimum balance maintenance: Only necessary operational funds kept online
- Real-time monitoring: Automated systems tracking all hot wallet transactions
- Multi-signature protection: Requiring multiple authorizations for outbound transfers
- Velocity controls: Limiting transaction frequency and amounts
- Automated cold storage transfers: Regular sweeps moving excess funds offline
- Network segregation: Isolated systems preventing lateral attack movement
Hot wallet risk management:
- Insurance coverage: Specific policies protecting online wallet contents
- Incident response procedures: Rapid response protocols for security breaches
- Load balancing: Distributing risk across multiple hot wallet systems
- Geographic redundancy: Multiple hot wallet locations for operational continuity
- Regular security assessments: Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning
Multi-Signature Wallet Implementation
Multi-signature wallets require multiple private key signatures for transaction authorization, preventing unauthorized access even if individual keys become compromised. Institutional-grade exchanges implement 3-of-5 or 5-of-7 multi-sig schemes.
Multi-signature benefits:
- Distributed control: No single person can authorize fund movements
- Redundancy protection: System remains operational if individual keys lost
- Internal controls: Segregation of duties preventing employee fraud
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting fiduciary requirements for fund custody
- Audit trails: Complete transaction authorization history for compliance reporting
Regulatory Frameworks Worldwide
Global Regulatory Approaches
Cryptocurrency regulation varies significantly across jurisdictions, ranging from comprehensive frameworks encouraging innovation to complete prohibitions restricting all digital asset activities. Understanding regional approaches helps traders navigate compliance requirements and platform availability.
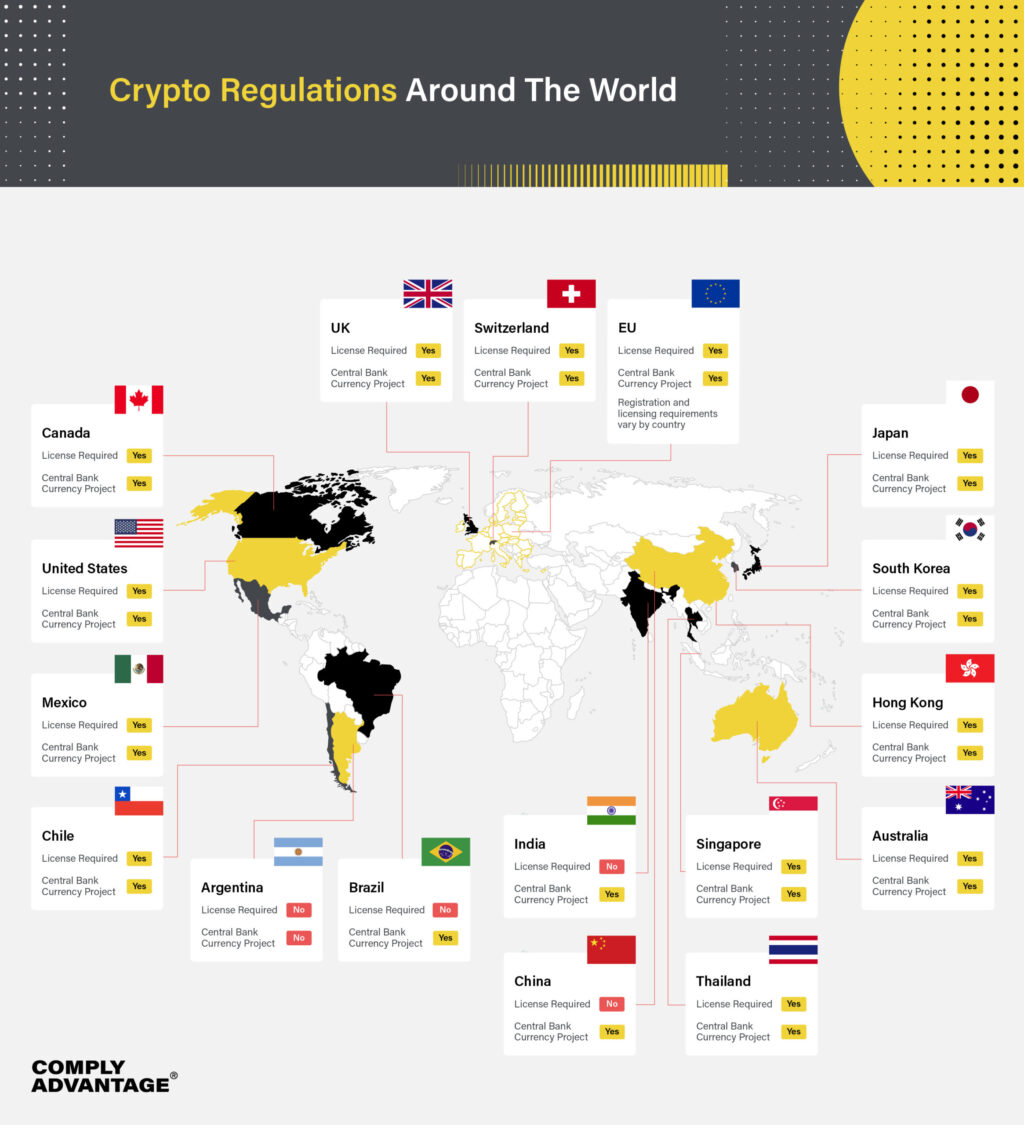
Regulatory classification approaches:
- Progressive frameworks: Clear guidelines encouraging responsible innovation
- Restrictive policies: Heavy regulations limiting cryptocurrency activities
- Prohibition regimes: Complete bans on cryptocurrency trading and services
- Evolving landscapes: Ongoing policy development and legislative processes
- Regulatory sandboxes: Limited testing environments for new technologies
Major regulatory trends include:
- Institutional adoption support: Frameworks enabling bank and pension fund participation
- Consumer protection emphasis: Enhanced disclosure and insurance requirements
- Anti-money laundering focus: Strengthened KYC and transaction reporting standards
- Stablecoin regulation: Specific rules for dollar-backed cryptocurrency issuance
- Cross-border cooperation: International coordination on regulatory standards
Regulatory Impact on Exchange Operations
Regulatory requirements directly influence exchange feature availability, supported cryptocurrencies, and operational procedures across different geographic markets. Compliance costs and legal complexity affect platform pricing and service quality.
Common regulatory requirements:
- Licensing obligations: Money transmission, securities dealer, or exchange operator licenses
- Capital requirements: Minimum reserves and ongoing financial reporting
- Customer protection: Segregated funds, insurance coverage, and dispute resolution
- Transaction monitoring: Suspicious activity reporting and sanctions screening
- Data protection: Privacy compliance and customer information security
- Audit requirements: Regular third-party assessments and regulatory examinations
US Cryptocurrency Regulations 2025
Federal Regulatory Framework
The United States implements comprehensive cryptocurrency regulation through multiple federal agencies including the SEC, CFTC, Treasury Department, and state-level money transmission authorities. Recent legislation including the GENIUS Act provides enhanced clarity for digital asset operations.
Key US regulatory developments 2025:
- GENIUS Act implementation: Stablecoin regulation requiring full reserve backing
- SEC Crypto Task Force: Enhanced guidance for securities classification
- CFTC digital commodities oversight: Expanded authority for Bitcoin and Ethereum
- Trump administration crypto working group: Federal policy coordination initiative
- Banking integration: OCC guidance enabling national bank crypto custody services
Federal agency responsibilities:
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): Regulates crypto assets deemed securities
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC): Oversees Bitcoin, Ethereum as commodities
- Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN): Anti-money laundering compliance
- Office of the Comptroller (OCC): National bank cryptocurrency service authorization
- Treasury Department/OFAC: Sanctions compliance and national security oversight
Money Transmitter Licensing
Cryptocurrency exchanges operating in the United States must obtain money transmitter licenses from individual states, creating complex compliance requirements varying across 50+ jurisdictions. Licensing costs and requirements significantly impact operational expenses.
State licensing requirements:
- Application procedures: Extensive documentation and background checks
- Capital requirements: Minimum net worth and bonding obligations
- Compliance infrastructure: AML programs and transaction monitoring systems
- Ongoing reporting: Regular financial statements and regulatory filings
- Examination processes: State regulator audits and compliance assessments
- Renewal obligations: Annual or periodic license renewal procedures
Major state frameworks:
- New York BitLicense: Comprehensive regulation for digital asset businesses
- California Digital Financial Assets Law: Licensing requirements effective 2026
- Wyoming Special Purpose Depository Institution: Crypto bank charter program
- Texas regulatory approach: Business-friendly policies encouraging innovation
- Florida digital asset legislation: Pro-innovation regulatory framework
Anti-Money Laundering Compliance
US cryptocurrency exchanges must implement comprehensive AML programs including customer identification procedures, suspicious activity monitoring, and regulatory reporting systems. Compliance costs typically represent 5-15% of operational expenses.
AML program requirements:
- Customer identification program (CIP): Identity verification for all account holders
- Know your customer (KYC) procedures: Enhanced due diligence for high-risk customers
- Suspicious activity reporting (SAR): Filing requirements for unusual transactions
- Currency transaction reporting (CTR): Reports for transactions exceeding $10,000
- Travel Rule compliance: Information sharing for transactions over $3,000
- OFAC sanctions screening: Real-time monitoring against prohibited parties
European Union Crypto Compliance
Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA)
The European Union’s MiCA framework provides comprehensive cryptocurrency regulation across all 27 member states, establishing uniform standards for crypto asset service providers (CASPs) and digital asset operations. Full implementation began January 2025.
MiCA key provisions:
- Unified licensing: Single passport enabling EU-wide operations
- Authorization requirements: Comprehensive applications for CASP licenses
- Capital adequacy: Minimum capital thresholds and ongoing financial monitoring
- Consumer protection: Segregation requirements and compensation schemes
- Governance standards: Risk management systems and internal controls
- Disclosure obligations: Transparent fee structures and risk warnings
CASP service categories under MiCA:
- Custody and administration: Safekeeping crypto assets on behalf of third parties
- Exchange services: Operating trading platforms for crypto asset transactions
- Execution of orders: Processing crypto asset transactions on behalf of clients
- Portfolio management: Discretionary management of crypto asset portfolios
- Investment advice: Providing personal recommendations regarding crypto assets
- Market making: Providing liquidity through continuous bid-offer prices
Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)
DORA establishes cybersecurity and operational resilience requirements for financial services including cryptocurrency platforms operating within the European Union. Compliance requirements focus on ICT risk management and third-party service oversight.
DORA compliance areas:
- ICT risk management: Comprehensive frameworks for technology risk assessment
- Incident reporting: Mandatory disclosure of significant operational disruptions
- Operational resilience testing: Regular assessments including penetration testing
- Third-party risk management: Due diligence requirements for service providers
- Information sharing: Cyber threat intelligence sharing with authorities
European Banking Authority Guidance
The European Banking Authority provides technical standards and supervisory guidance for cryptocurrency service providers operating under MiCA and traditional banking regulations. EBA guidance addresses operational requirements and consumer protection measures.
EBA guidance areas:
- Authorization procedures: Application processes and assessment criteria
- Ongoing supervision: Monitoring requirements and examination procedures
- Consumer protection: Fair treatment and disclosure requirements
- Operational requirements: Systems, controls, and governance standards
- Cross-border coordination: Supervisory cooperation across member states
Asia-Pacific Regional Regulations
Singapore Regulatory Approach
Singapore implements comprehensive cryptocurrency regulation through the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) Payment Services Act, providing clear frameworks for digital asset businesses while maintaining high compliance standards. Singapore attracts global crypto companies seeking regulatory certainty.
Singapore compliance requirements:
- Payment Service Provider licensing: Mandatory registration for crypto exchanges
- Capital requirements: Minimum base capital and ongoing financial obligations
- Technology risk management: Robust systems and cybersecurity frameworks
- AML/CFT compliance: Comprehensive programs preventing financial crime
- Consumer protection: Clear disclosures and fair treatment standards
- Business conduct standards: Professional competency and ethical requirements
MAS regulatory benefits:
- Clear guidelines: Comprehensive guidance documents and consultation processes
- Innovation support: Regulatory sandbox for fintech experimentation
- International recognition: Strong reputation attracting global businesses
- Stable political environment: Predictable regulatory and legal frameworks
- Banking relationships: Established financial infrastructure supporting crypto businesses
Japan Virtual Asset Regulations
Japan pioneered comprehensive cryptocurrency regulation through amendments to the Payment Services Act and Financial Instruments and Exchange Act, creating frameworks balancing innovation with consumer protection. Japanese regulations influence global regulatory development.
Japanese regulatory features:
- Virtual currency exchange licensing: Comprehensive authorization requirements
- Customer asset segregation: Mandatory separation of customer and exchange funds
- Cold storage requirements: Offline storage for majority of customer assets
- Insurance obligations: Coverage requirements for hot wallet cryptocurrency holdings
- Financial reporting: Regular disclosures and third-party audits
- Business conduct standards: Fair dealing and conflict of interest management
Hong Kong and China Approaches
Hong Kong develops pro-innovation cryptocurrency regulation while mainland China maintains comprehensive prohibitions on cryptocurrency trading and services. This regulatory divergence creates complex compliance challenges for regional operations.
Hong Kong developments:
- Securities and Futures Commission oversight: Licensing for professional investors
- Retail investor access: Gradual expansion of cryptocurrency investment options
- Stablecoin regulation: Comprehensive framework for Hong Kong dollar stablecoins
- Banking support: Enhanced cryptocurrency business banking relationships
China restrictions:
- Complete trading prohibition: Comprehensive bans on cryptocurrency exchanges
- Mining restrictions: Elimination of cryptocurrency mining operations
- Payment prohibitions: Financial institutions forbidden from crypto services
- Digital yuan development: Central bank digital currency alternative
Exchange Insurance and Protection
Insurance Coverage Types
Cryptocurrency exchange insurance protects against various risks including cyber attacks, employee theft, operational errors, and custody failures. Coverage types and limits vary significantly between platforms and may not protect against all loss scenarios.
Common insurance categories:
- Cyber liability: Protection against hacking and digital theft
- Crime coverage: Employee dishonesty and internal fraud protection
- Errors and omissions: Operational mistakes and professional liability
- Directors and officers: Management decision liability coverage
- General liability: Third-party claims and business operations
- Property insurance: Physical damage to equipment and facilities
SAFU and Exchange-Specific Funds
Binance’s Secure Asset Fund for Users (SAFU) represents the largest exchange-operated insurance fund, maintaining over $1 billion in reserves for customer protection. Other exchanges implement similar but smaller emergency funds.

Exchange emergency funds comparison:
- Binance SAFU: $1+ billion fund covering customer losses from security breaches
- OKX Reserve Fund: Dedicated fund protecting against extreme market conditions
- Bybit Insurance Fund: Auto-deleveraging protection for derivatives trading
- BitMEX Insurance Fund: Coverage for unfilled bankruptcy orders
- Huobi Protection Fund: Customer asset protection against platform risks
Fund limitations and exclusions:
- Coverage scope: May not protect against all types of losses
- Reimbursement procedures: Complex claims processes and documentation requirements
- Market risk exclusions: No protection against cryptocurrency price volatility
- Regulatory risks: Potential government seizures not covered
- User error protection: Limited coverage for customer mistakes
Traditional Insurance Integration
Leading exchanges increasingly secure traditional insurance coverage from established providers including Lloyd’s of London, AIG, and specialized cyber insurance underwriters. Traditional insurance provides additional credibility and regulatory compliance benefits.
Traditional insurance advantages:
- Regulatory recognition: Accepted by institutional investors and regulators
- Coverage expertise: Established claims handling and risk assessment
- Financial stability: Strong balance sheets supporting large claims
- Comprehensive protection: Broader coverage beyond cryptocurrency-specific risks
- Legal frameworks: Established contract law and dispute resolution processes
Proof of Reserves and Transparency
Proof of Reserves Methodology
Proof of reserves provides cryptographic verification that exchanges hold sufficient cryptocurrency to meet all customer withdrawal requests, addressing concerns about fractional reserve practices. Regular attestations demonstrate platform solvency without revealing individual customer information.
Proof of reserves process:
- Asset inventory: Complete accounting of all exchange-held cryptocurrencies
- Customer liability calculation: Total customer balances across all accounts
- Cryptographic proof generation: Mathematical verification of reserve adequacy
- Third-party auditing: Independent verification of reserve calculations
- Public disclosure: Regular publication of reserve status updates
- Ongoing monitoring: Continuous verification of reserve maintenance
Leading exchange implementations:
- Kraken: Monthly proof of reserves with detailed methodology disclosure
- Binance: Regular attestations covering Bitcoin, Ethereum, and major altcoins
- Coinbase: Quarterly reserve disclosures integrated with SEC reporting
- OKX: Real-time reserve monitoring with public verification tools
- Gate.io: Regular proof of reserves across supported cryptocurrencies
Transparency Initiatives
Exchange transparency extends beyond proof of reserves to include operational disclosures, security practices, and business relationship information. Enhanced transparency builds user trust while supporting regulatory compliance objectives.
Transparency best practices:
- Security incident disclosure: Public reporting of security breaches and responses
- Operational metrics: Trading volume, user count, and financial performance data
- Regulatory relationships: Clear disclosure of licensing and compliance status
- Business partnerships: Transparency about banking relationships and service providers
- Governance structures: Information about ownership, management, and decision-making
- Risk management: Policies and procedures for operational risk mitigation
Independent Auditing
Third-party security audits and financial examinations provide independent verification of exchange operations and control effectiveness. Regular auditing supports regulatory compliance while identifying potential vulnerabilities.
Audit types and frequency:
- Security audits: Annual penetration testing and vulnerability assessments
- Financial audits: Quarterly or annual examination of financial controls
- Compliance audits: Regulatory examination of AML and operational procedures
- SOC 2 attestations: Annual evaluation of security and operational controls
- Proof of reserves verification: Regular independent confirmation of reserve adequacy
Personal Security Best Practices
Account Security Configuration
Personal account security requires multi-layered protection including strong authentication, device management, and withdrawal controls. Professional traders implement institutional-grade security practices protecting substantial cryptocurrency holdings.
Essential account security measures:
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Hardware keys preferred over SMS authentication
- Strong unique passwords: Complex passwords unique to each exchange account
- Email security: Secure email accounts with 2FA protection
- Device management: Regular monitoring of authorized devices and sessions
- Withdrawal whitelisting: Pre-approved addresses with mandatory waiting periods
- API key security: Limited permissions and IP address restrictions
- Regular password updates: Periodic password changes and security reviews
Cold Storage for Personal Holdings
Personal cold storage provides maximum security for long-term cryptocurrency holdings, eliminating online attack vectors while maintaining complete control over private keys. Hardware wallets offer optimal balance between security and usability.
Personal cold storage options:
- Hardware wallets: Ledger, Trezor, and other dedicated security devices
- Paper wallets: Offline key generation and physical storage
- Air-gapped computers: Dedicated offline devices for key management
- Multi-signature setups: Distributed key management across multiple devices
- Bank safety deposit boxes: Physical security for backup materials
- Geographic distribution: Multiple secure locations for redundancy
Cold storage best practices:
- Backup procedures: Multiple copies of recovery phrases in secure locations
- Physical security: Protection against theft, fire, and natural disasters
- Regular testing: Periodic verification of backup and recovery procedures
- Update management: Firmware updates and security patch installation
- Inheritance planning: Secure methods for family access if needed
Phishing and Social Engineering Prevention
Cryptocurrency-focused phishing attacks target exchange credentials, private keys, and personal information through sophisticated social engineering techniques. Awareness and verification procedures prevent most attack attempts.
Common attack vectors:
- Fake websites: Impersonating legitimate exchange domains
- Email phishing: Official-appearing messages requesting credentials
- Social media scams: Fake customer support and investment opportunities
- Phone attacks: SIM swapping and impersonation calls
- Malware distribution: Infected software targeting cryptocurrency users
- Physical attacks: Targeted individuals for crypto asset theft
Prevention strategies:
- URL verification: Always type exchange URLs directly or use bookmarks
- Email authentication: Verify sender authenticity through official channels
- Customer support verification: Contact exchanges through verified channels only
- Software integrity: Download applications from official sources only
- Public WiFi avoidance: Avoid cryptocurrency activities on unsecured networks
- Privacy protection: Limit public disclosure of cryptocurrency activities
Common Security Threats and Prevention
Exchange-Level Threats
Cryptocurrency exchanges face sophisticated attack vectors including advanced persistent threats, insider attacks, and infrastructure vulnerabilities. Understanding common threats helps evaluate platform security measures and risk levels.
Major threat categories:
- Cyber attacks: Sophisticated hacking attempts targeting hot wallets and systems
- Insider threats: Employee misconduct and unauthorized access
- Infrastructure attacks: DDoS attacks and system availability disruptions
- Supply chain compromises: Third-party service provider vulnerabilities
- Regulatory risks: Government actions affecting operations
- Operational risks: Technical failures and human errors
2024-2025 Security Incidents Analysis
Major security incidents in 2024-2025 provide insights into evolving threat landscapes and effective protection strategies. Learning from recent incidents helps improve personal and platform security measures.
Notable 2024-2025 incidents:
- February 2025: $1.5 billion North Korean attack on Dubai-based exchange cold wallet
- Ongoing threats: $2.17+ billion stolen across CEXs, DeFi platforms, and bridges
- Attack evolution: Advanced phishing and supply chain compromise techniques
- Cold storage vulnerabilities: Sophisticated attacks bypassing traditional protections
- Multi-sig defeats: Complex attacks overcoming multiple signature protections
Lessons learned:
- No system is invulnerable: Even cold storage faces sophisticated attack vectors
- Insider risks remain significant: Employee access controls require constant vigilance
- Supply chain security critical: Third-party service providers present attack surfaces
- User education essential: Social engineering remains primary attack vector
- Incident response importance: Rapid detection and response minimize damage
Emerging Threat Landscape
Cryptocurrency security threats continue evolving with artificial intelligence, quantum computing developments, and increasing institutional adoption creating new attack vectors and defense requirements. Staying informed about emerging threats helps maintain effective security postures.
Future security considerations:
- AI-powered attacks: Automated reconnaissance and social engineering
- Quantum computing threats: Potential cryptographic vulnerabilities
- Institutional targeting: Sophisticated attacks on high-value targets
- Regulatory compliance attacks: Exploiting compliance processes and procedures
- Cross-chain vulnerabilities: Bridge protocols and interoperability risks
Regulatory Compliance for Traders
Individual Trader Obligations
Individual cryptocurrency traders must comply with tax reporting, anti-money laundering regulations, and jurisdiction-specific restrictions regardless of exchange location. Compliance obligations vary significantly based on residence, trading volume, and asset types.
Common individual compliance requirements:
- Tax reporting: Capital gains and income tax obligations for all transactions
- Transaction documentation: Detailed records supporting tax return preparation
- Source of funds: Documentation for large deposits and trading activities
- Reporting thresholds: Disclosure requirements for substantial holdings or transactions
- Cross-border restrictions: Compliance with international sanctions and restrictions
- Professional obligations: Additional requirements for financial industry professionals
Cross-Border Trading Compliance
International cryptocurrency trading creates complex compliance obligations involving multiple jurisdictions, tax treaties, and reporting requirements. Professional advice becomes essential for substantial cross-border activities.
Cross-border considerations:
- Tax treaty benefits: Avoiding double taxation through bilateral agreements
- Foreign account reporting: FATCA, FBAR, and similar international disclosure requirements
- Transfer pricing: Documentation for related party transactions
- Withholding tax obligations: Foreign exchange and service provider tax withholding
- Exchange control compliance: Currency control regulations and reporting requirements
Professional Trading Compliance
Professional cryptocurrency traders and investment managers face enhanced compliance obligations including registration requirements, fiduciary duties, and institutional reporting standards. Compliance costs and complexity increase significantly for professional operations.
Professional compliance areas:
- Investment adviser registration: SEC or state registration for advisory services
- Broker-dealer obligations: Registration requirements for trading services
- Custody regulations: Fiduciary requirements for customer asset safekeeping
- Record keeping: Enhanced documentation and audit trail maintenance
- Client protection: Suitability assessments and disclosure obligations
Future of Crypto Security and Regulation
Technology Evolution Impact
Emerging technologies including quantum computing, artificial intelligence, and advanced cryptography will reshape cryptocurrency security requirements and regulatory frameworks. Early adoption of next-generation security measures provides competitive advantages.
Technology trends affecting security:
- Quantum-resistant cryptography: Preparation for quantum computing threats
- Zero-knowledge proofs: Enhanced privacy while maintaining compliance
- Multi-party computation: Distributed security without centralized control
- Biometric authentication: Enhanced user verification and access control
- AI-powered monitoring: Automated threat detection and response systems
- Decentralized identity: Self-sovereign identity management systems
Regulatory Convergence Trends
Global regulatory frameworks increasingly coordinate standards and procedures, creating more consistent compliance requirements across jurisdictions. International cooperation improves while maintaining local sovereignty over financial regulation.
Convergence developments:
- FATF travel rule standardization: Uniform information sharing requirements globally
- Basel Committee crypto guidelines: Banking sector cryptocurrency risk management
- IOSCO recommendations: Securities regulator coordination on digital assets
- G20 policy coordination: Major economy alignment on regulatory approaches
- Cross-border enforcement cooperation: Joint investigations and information sharing
- Technical standards harmonization: API protocols and reporting formats
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central bank digital currencies development influences cryptocurrency regulation by providing government-controlled alternatives to private digital assets. CBDC implementation may affect exchange operations, privacy expectations, and regulatory requirements.
CBDC regulatory implications:
- Competitive pressure: Official digital currencies competing with cryptocurrencies
- Enhanced monitoring: Government visibility into all digital transactions
- Privacy considerations: Balancing surveillance capabilities with individual privacy
- Cross-border payments: International CBDC coordination affecting crypto demand
- Financial inclusion: Digital currency access potentially reducing cryptocurrency adoption
- Innovation impact: Government digital assets spurring or constraining private innovation
Industry Self-Regulation Evolution
Cryptocurrency industry self-regulation initiatives complement government frameworks while providing practical compliance guidance and best practices. Industry associations increasingly influence regulatory development through engagement and standard-setting.
Self-regulation initiatives:
- Blockchain Association: US industry advocacy and policy development
- Crypto Council for Innovation: Global policy research and advocacy
- Digital Chamber: Blockchain technology policy and education
- Association for Digital Asset Markets: European industry representation
- Japan Virtual Currency Exchange Association: Self-regulatory organization model
- Singapore FinTech Association: Regional industry coordination and standards
Frequently Asked Questions
How secure are major crypto exchanges?
Major cryptocurrency exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken implement enterprise-grade security measures including cold storage, multi-signature wallets, and comprehensive insurance coverage. However, no exchange is completely immune to sophisticated attacks, making personal security practices essential.
What should I look for in exchange security features?
Prioritize exchanges offering cold storage (90%+ of funds offline), multi-factor authentication, proof of reserves, regulatory compliance, and comprehensive insurance coverage. Additionally, examine the platform’s security track record, incident response history, and transparency regarding security practices.
Are crypto exchanges regulated?
Yes, legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges operate under various regulatory frameworks depending on their location and services offered. US exchanges require money transmitter licenses, while EU platforms must comply with MiCA regulations. Always verify an exchange’s regulatory status before depositing funds.
What is proof of reserves and why does it matter?
Proof of reserves provides cryptographic verification that exchanges hold sufficient cryptocurrency to meet all customer withdrawal requests. This transparency measure helps prevent fractional reserve practices and builds confidence that your funds are actually held by the exchange rather than lent out or misappropriated.
How can I protect my crypto beyond exchange security?
Use hardware wallets for long-term storage, enable two-factor authentication with hardware keys, create strong unique passwords, whitelist withdrawal addresses, and maintain offline backups of recovery phrases. Never share private keys or seed phrases with anyone, including customer support representatives.
What happens if my exchange gets hacked?
Exchange responses to security breaches vary significantly based on their insurance coverage, reserve funds, and legal obligations. Platforms like Binance maintain SAFU emergency funds, while Coinbase provides insurance coverage. However, recovery is not guaranteed, emphasizing the importance of personal security measures.
Are there regulatory differences between countries?
Yes, cryptocurrency regulations vary dramatically between jurisdictions. The US implements complex multi-agency oversight, the EU provides unified MiCA frameworks, Singapore offers clear guidelines, while China prohibits cryptocurrency activities entirely. Always research local regulations before trading.
Should I use regulated or unregulated exchanges?
Regulated exchanges typically provide better consumer protection, insurance coverage, and legal recourse, but may have higher fees and stricter verification requirements. Unregulated platforms may offer more features and privacy but carry higher risks of sudden shutdowns or fund loss.
How do I verify an exchange’s security claims?
Review third-party security audits, proof of reserves publications, regulatory filings, insurance documentation, and incident response history. Look for SOC 2 Type II certifications, independent security assessments, and transparent communication about security practices and any past incidents.
What are the biggest risks when using crypto exchanges?
Primary risks include exchange hacks, regulatory shutdowns, exit scams, market manipulation, technical failures, and personal account compromises. Mitigate risks through diversification across multiple platforms, personal security measures, and keeping only necessary funds on exchanges for active trading.
Choose Secure Exchanges
Select cryptocurrency exchanges based on comprehensive security evaluations, regulatory compliance status, and alignment with your trading requirements and risk tolerance. No single platform excels in all areas, making careful evaluation essential for optimal platform selection.
For maximum security and regulatory compliance:
- Coinbase: US-regulated platform with institutional-grade security and insurance coverage
- Kraken: Proven security track record with zero successful hacks and transparent operations
- Gemini: Regulated US exchange with strong security focus and conservative approach
For comprehensive features with strong security:
- Binance: Largest exchange with extensive security infrastructure and SAFU protection
- OKX: Advanced trading features with robust security measures and global presence
- Bybit: Derivatives-focused platform with strong security and insurance fund protection
Security evaluation checklist:
- Regulatory compliance: Verify licensing and regulatory standing in operating jurisdictions
- Security track record: Research past incidents and response effectiveness
- Insurance coverage: Understand protection levels and coverage limitations
- Cold storage implementation: Confirm majority of funds stored offline securely
- Transparency measures: Look for proof of reserves and regular security disclosures
- User security tools: Evaluate available protection features and requirements
Risk management strategies:
- Portfolio diversification: Spread holdings across multiple exchanges and storage methods
- Minimum balance maintenance: Keep only necessary trading funds on exchanges
- Regular security audits: Monitor account activity and security settings monthly
- Stay informed: Follow security news and platform updates regularly
- Professional advice: Consult security experts for substantial holdings or complex situations
Action steps for enhanced security:
- Research platform security: Evaluate multiple exchanges using security criteria above
- Enable all security features: Implement 2FA, withdrawal whitelist, and device management
- Establish cold storage: Set up hardware wallets for long-term holdings
- Create emergency procedures: Develop incident response plans and backup access methods
- Monitor and maintain: Regular security reviews and update procedures as needed
Remember: Even the most secure exchanges face sophisticated threats. Combine exchange security with personal protection measures including cold storage, strong authentication, and continuous vigilance against phishing and social engineering attacks.
Ready to start trading on secure platforms? Sign up with Binance for comprehensive security features and global liquidity, or choose Coinbase for maximum regulatory compliance and institutional-grade protection in the United States.
Begin with security-focused crypto exchanges that prioritize user protection while providing advanced trading features and competitive fee structures for optimal cryptocurrency investment experiences.
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves substantial risk of loss and may not be suitable for all investors. Security measures cannot eliminate all risks including platform failures, regulatory changes, and market volatility. Past security performance does not guarantee future protection.
Risk Warning: No exchange or security measure provides complete protection against all threats. Always diversify holdings across multiple platforms and storage methods. Never invest more than you can afford to lose entirely.
Educational Purpose: This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment, security, or legal advice. Consult qualified security professionals and legal advisors before making decisions regarding cryptocurrency investments and security procedures.
