How Does a Crypto Exchange Work? A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Crypto Trading Platforms
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
- Understand what a crypto exchange is and why it matters
- Learn about the different types of exchanges and their unique features
- Discover core processes: matching engines, order books, and liquidity management
- See how KYC, AML, deposits, withdrawals, and fees work
- Clarify key order types and how trading execution happens
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Are the Different Types of Crypto Exchanges?
- What Processes Power a Crypto Exchange Behind the Scenes?
- How Do Account Registration, KYC, and AML Verification Work?
- How Do Deposits and Withdrawals Function (Fiat vs Crypto)?
- What is an Order Book and How Does Order Matching Happen?
- FAQ
Introduction
Cryptocurrency exchanges serve as the fundamental infrastructure connecting digital asset traders and investors worldwide. These sophisticated platforms function as digital marketplaces where users can buy, sell, and trade various cryptocurrencies, from Bitcoin and Ethereum to thousands of alternative tokens. Understanding how crypto exchanges operate becomes essential for anyone seeking to participate in the digital economy, whether as a beginner taking first steps into cryptocurrency or an experienced trader optimizing investment strategies. For a detailed breakdown of what a crypto exchange is and its role in the crypto ecosystem, see the referenced guide.
At its core, a cryptocurrency exchange operates through complex technological systems that process millions of transactions daily while maintaining security standards and regulatory compliance. These platforms bridge the gap between traditional financial systems and the emerging blockchain ecosystem, enabling seamless conversion between fiat currencies and digital assets. If you’re interested in a step-by-step guide specifically tailored for newcomers, check out this in-depth walkthrough for beginners.

What Are the Different Types of Crypto Exchanges?
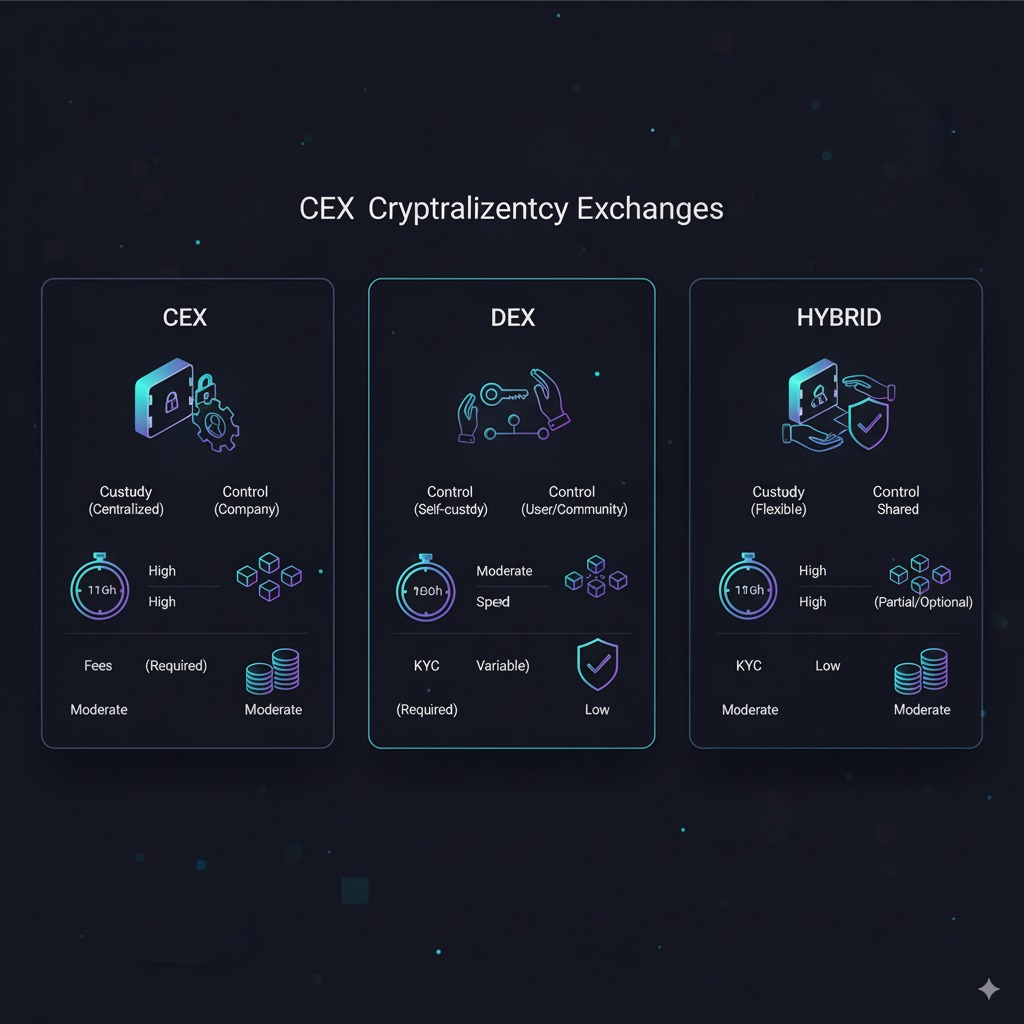
The cryptocurrency exchange landscape consists of three primary categories, each offering distinct advantages for different user needs and trading preferences.
Centralized Exchanges (CEX) represent the most common type of trading platform, operating under traditional business models where the exchange maintains full control over user funds and trading operations. These platforms—including Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken—provide user-friendly interfaces, high liquidity, and comprehensive customer support. Centralized exchanges offer features such as fiat-to-crypto conversion, advanced trading tools, and insurance coverage for user deposits. For insights on choosing the best centralized platform, see the guide, and view comparison details at Top Crypto Exchanges 2025 Comparison.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) operate through smart contracts on blockchain networks, eliminating the need for intermediary control over user funds. Platforms like Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap allow users to trade directly from their personal wallets while maintaining custody of their assets throughout the transaction process. These exchanges provide greater privacy and resistance to censorship but typically require more technical knowledge to navigate effectively.
Hybrid Exchanges combine elements from both centralized and decentralized models, attempting to balance user convenience with decentralized principles. These platforms may offer centralized order matching with decentralized settlement or provide optional custody services alongside self-custody options. To understand how leading exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, and OKX fit into these categories, explore platform-specific reviews at Binance, Coinbase, and OKX.
| Exchange Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized | High liquidity, user-friendly, fiat support, customer service | Custody risk, regulatory exposure, potential downtime |
| Decentralized | Self-custody, privacy, censorship resistance | Lower liquidity, technical complexity, limited fiat support |
| Hybrid | Balanced approach, flexible options | Complex architecture, varying trust models |
Understanding these fundamental differences helps users select appropriate platforms based on their trading experience, security preferences, and regulatory requirements.
What Processes Power a Crypto Exchange Behind the Scenes?
Cryptocurrency exchanges rely on sophisticated technological infrastructure operating continuously to facilitate seamless trading experiences. These underlying processes work together to ensure platform reliability, security, and efficiency.
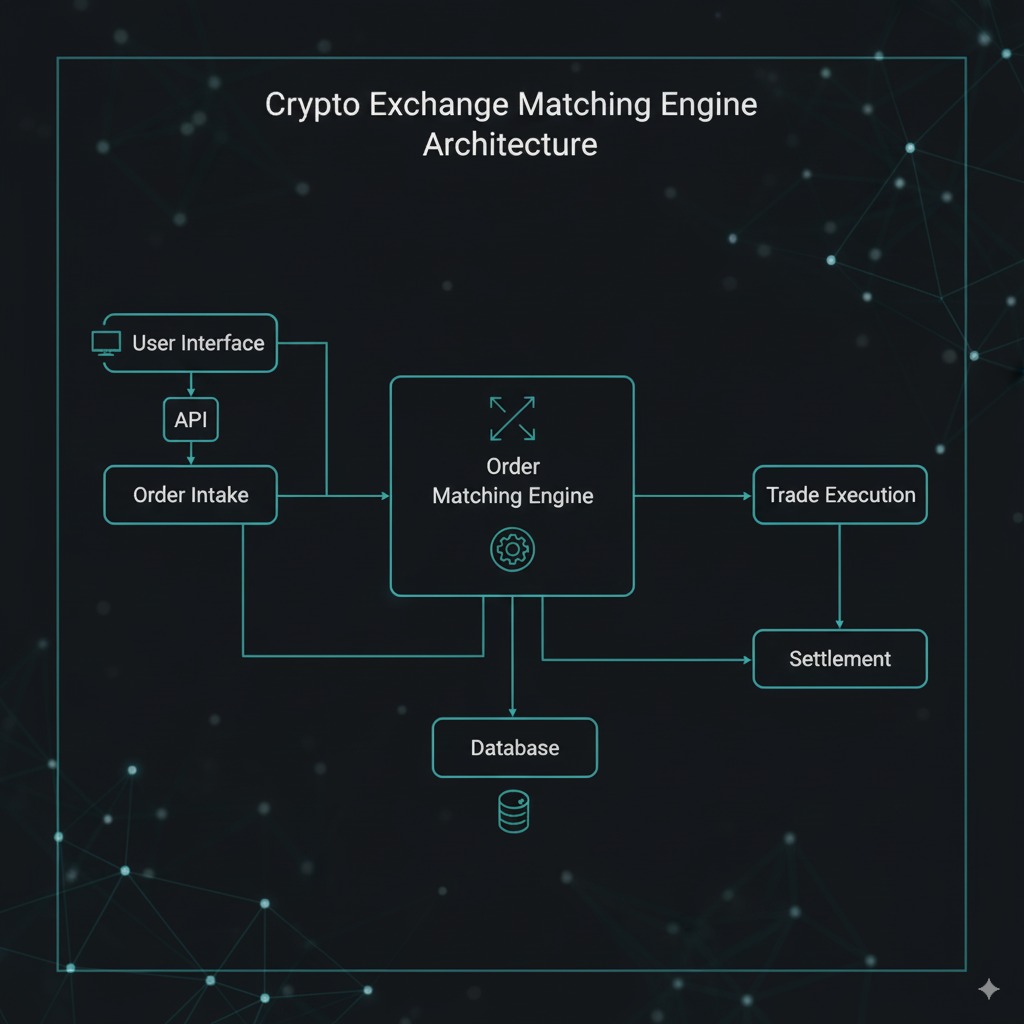
The matching engine serves as the heart of exchange operations, processing buy and sell orders at incredible speeds. This system matches compatible orders based on price and timing parameters, executing trades within milliseconds. Modern exchanges utilize advanced algorithms capable of processing hundreds of thousands of orders per second while maintaining chronological accuracy.
Order book management systems maintain real-time records of all pending buy and sell orders, organizing them by price level and timestamp. These databases update instantaneously as new orders arrive and existing orders execute or cancel, providing traders with current market depth information essential for informed decision-making. To explore more about how order books, order types, and trading execution work, check this overview of basic trading knowledge.
Liquidity management involves partnerships with market makers and liquidity providers who ensure sufficient trading volume across various cryptocurrency pairs. Exchanges implement sophisticated algorithms to balance order flow and maintain tight bid-ask spreads, particularly during volatile market conditions.
Security protocols encompass multiple layers including cold storage systems for cryptocurrency reserves, multi-signature wallet technology, and advanced encryption methods protecting user data and funds. These systems undergo regular audits and penetration testing to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Security is a core concern—find best practices and regulatory guidelines here.
Blockchain integration connects exchanges to various blockchain networks, enabling deposit and withdrawal functionality across numerous cryptocurrencies. This infrastructure must accommodate different blockchain architectures, consensus mechanisms, and transaction speeds while maintaining security standards.
These interconnected systems operate continuously, processing transactions worth billions of dollars daily while maintaining the reliability and security standards users expect from professional trading platforms.
How Do Account Registration, KYC, and AML Verification Work?
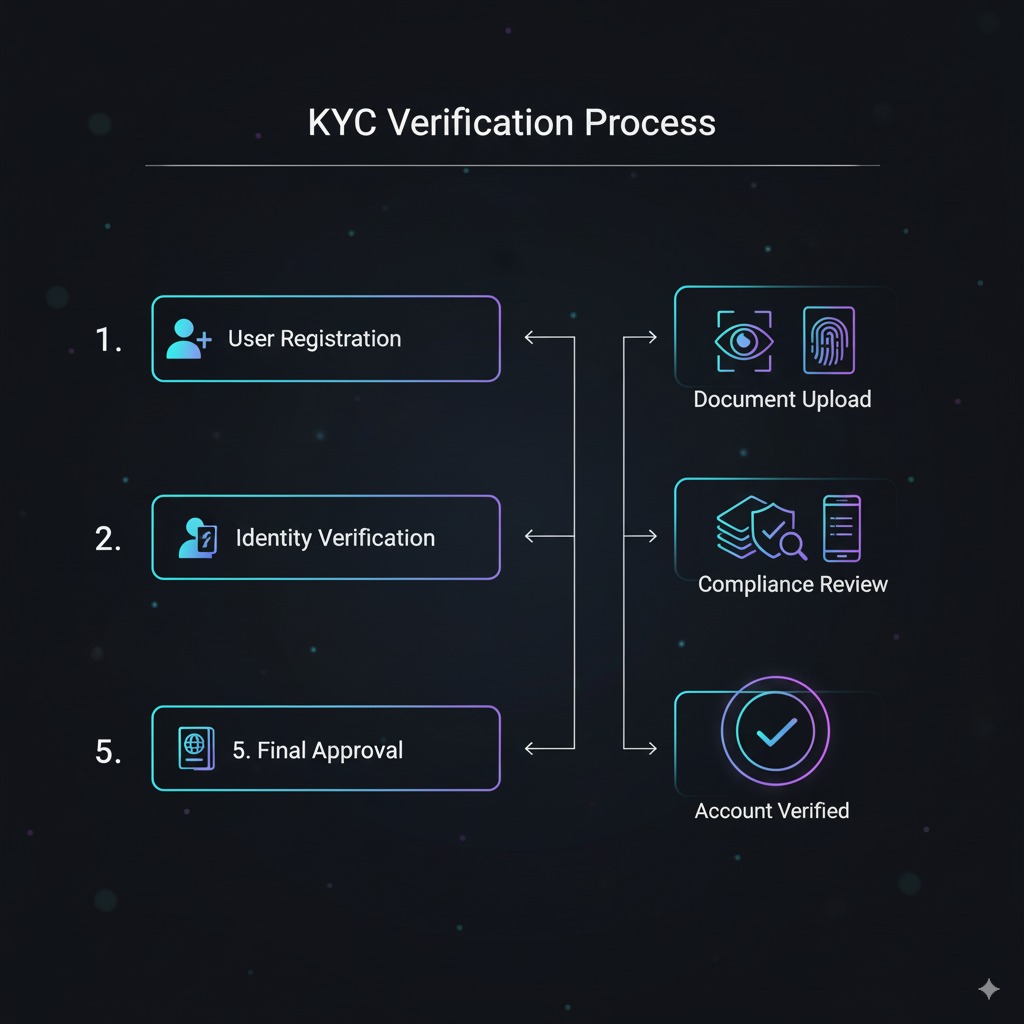
Account creation and verification processes on cryptocurrency exchanges involve multiple steps designed to ensure regulatory compliance while protecting both users and platforms from illicit activities. For those starting out, a primer on account setup and security can be found here.
The registration process begins with users providing basic information including email addresses, chosen usernames, and secure passwords. Most platforms implement two-factor authentication (2FA) requirements during initial setup, adding an essential security layer protecting accounts from unauthorized access.
Know Your Customer (KYC) verification requires users to submit government-issued identification documents such as passports, driver’s licenses, or national identity cards. Advanced verification systems utilize automated document scanning technology combined with human review processes to authenticate submitted credentials. Users typically photograph or scan identity documents alongside selfies for facial recognition verification.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) screening involves background checks against international databases containing information about politically exposed persons, sanctioned individuals, and entities associated with criminal activities. These checks occur automatically during registration and continue throughout the user’s relationship with the exchange platform.
Verification levels determine trading limits and available features. Basic verification typically allows limited cryptocurrency trading, while enhanced verification enables higher transaction limits, fiat currency operations, and access to advanced trading features. Some exchanges offer institutional verification tiers requiring additional documentation such as business registration certificates and beneficial ownership information.
The verification timeline varies significantly between exchanges, ranging from instant automated approval for basic levels to several days for comprehensive institutional verification. Regulatory requirements differ across jurisdictions, influencing the specific documentation and verification procedures each exchange implements. If you want to go deeper into compliance and regulatory frameworks, see this legal aspects resource.
These processes, while sometimes perceived as cumbersome, provide essential protection against fraud, money laundering, and regulatory violations that could compromise exchange operations and user security.
How Do Deposits and Withdrawals Function (Fiat vs Crypto)?
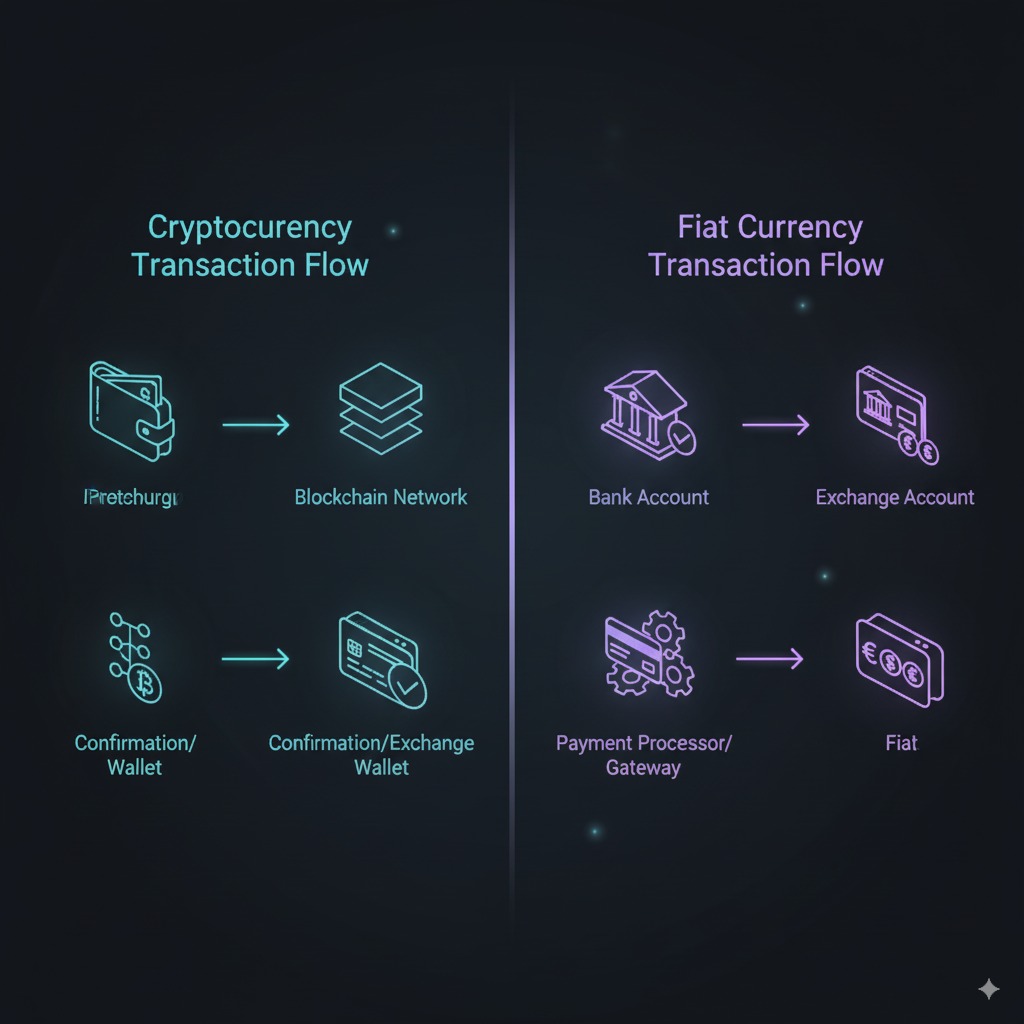
Deposit and withdrawal mechanisms represent critical exchange functions enabling users to move funds between traditional banking systems, personal wallets, and exchange accounts through various methods tailored to different asset types.
Cryptocurrency deposits occur through blockchain transactions where users send digital assets from external wallets to exchange-provided addresses. Each cryptocurrency requires specific network protocols and confirmation requirements. Bitcoin transactions typically require 3-6 confirmations (approximately 30-60 minutes), while Ethereum transactions need 12 confirmations (roughly 3-5 minutes). Some platforms offer instant crediting for smaller amounts while requiring additional confirmations for larger deposits.
Fiat currency deposits utilize traditional banking infrastructure including wire transfers, credit card payments, and automated clearing house (ACH) transfers. Wire transfers typically process within 1-3 business days but may incur fees ranging from $15-50 USD. Credit card deposits provide instant availability but carry higher processing fees, often 3-5% of transaction amounts. ACH transfers offer lower fees but require 3-7 business days for completion.
Cryptocurrency withdrawals involve blockchain transactions from exchange hot wallets to user-specified addresses. Exchanges implement multiple security measures including email confirmations, 2FA verification, and withdrawal delays for enhanced security. Network fees vary significantly based on blockchain congestion, ranging from less than $1 for networks like Polygon to $20-100+ during Ethereum network congestion periods.
Fiat currency withdrawals process through traditional banking channels with verification requirements and processing timeframes varying by jurisdiction and withdrawal amount. Bank transfers typically complete within 1-5 business days, while some exchanges offer expedited processing for verified users. Withdrawal limits range from $2,000-50,000+ daily depending on account verification levels.
Processing times and fees differ substantially between deposit and withdrawal methods, influencing user preferences based on urgency, cost considerations, and geographic location. Understanding these mechanisms helps users plan transactions effectively and manage associated costs. For in-depth comparisons of fees and how to save on costs, refer to this overview of exchange fees.
What is an Order Book and How Does Order Matching Happen?
The order book serves as the fundamental mechanism through which cryptocurrency exchanges organize and execute trades, providing transparency into market depth and price discovery processes essential for effective trading strategies. If you want a detailed beginner’s breakdown, see this comprehensive guide.
An order book consists of two main components: buy orders (bids) arranged from highest to lowest price, and sell orders (asks) organized from lowest to highest price. This structure creates a visual representation of supply and demand at various price levels, enabling traders to assess market sentiment and liquidity conditions before placing orders.
Each order entry contains specific information including the price level, quantity of cryptocurrency offered or sought, and timestamp indicating when the order entered the system. The difference between the highest bid price and lowest ask price creates the “spread,” which indicates market liquidity and trading costs.
Order matching occurs automatically when compatible buy and sell orders meet price and quantity criteria. The matching engine processes orders based on price-time priority, meaning orders offering better prices execute first, followed by earlier timestamps for orders at identical price levels. This system ensures fair and transparent order execution for all market participants.
“Market makers” provide liquidity by placing orders away from current market prices, earning profits from bid-ask spreads while reducing market volatility. “Market takers” consume existing liquidity by placing orders that execute immediately against available orders in the order book.
When a market buy order arrives, the matching engine executes it against the lowest-priced sell orders available, potentially filling against multiple orders if necessary to complete the full quantity requested. Conversely, market sell orders execute against the highest-priced buy orders available until the order is completely filled or the spread is encountered.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a centralized and decentralized crypto exchange?
Centralized exchanges (CEX) hold custody of user funds and offer user-friendly tools with higher liquidity, while decentralized exchanges (DEX) allow direct trades from users’ wallets and prioritize privacy and self-custody but require more technical knowledge and usually have lower liquidity.
Is KYC always required to use a crypto exchange?
Most centralized exchanges require KYC to comply with regulation, especially for fiat transactions and higher trading limits. Some DEXs do not require KYC, though certain features might be restricted.
How do I choose the right crypto exchange platform?
Consider your priorities: If you need fiat support, advanced trading tools, and responsive customer service, a CEX might be suitable. If you want self-custody and privacy, try a DEX. Compare features, security, and fees with guides like this resource.
What are network fees and how can I minimize them?
Network fees are blockchain charges for moving crypto on-chain. Fees depend on network congestion and the specific cryptocurrency. Use networks like Polygon or Tron for lower fees, plan withdrawals during low congestion, and consult exchange fee guides for tips.
What security features should I look for in a crypto exchange?
Seek exchanges that use cold storage, multi-signature wallets, two-factor authentication, regular audits, and have strong regulatory compliance. Learn more via security best practices.
