Crypto Exchange Fees Guide 2025: Compare Trading Costs & Save Money
Crypto exchange fees significantly impact your trading profitability, with costs ranging from 0.01% to 0.75% per trade across major platforms. Understanding fee structures helps you save hundreds or thousands of dollars annually while maximizing investment returns through strategic exchange selection.
Trading fees represent the largest expense for active cryptocurrency traders, often exceeding 2-3% of total portfolio value annually. Professional traders minimize costs through maker-taker optimization, VIP tier progression, and exchange token utilization on platforms offering comprehensive trading features.
The global crypto exchange market processes over $3 trillion in monthly volume, generating billions in fee revenue through various cost structures. Smart traders leverage fee optimization strategies, exchange tokens, and volume-based discounts to reduce total trading expenses by 30-50% compared to retail rates.
This comprehensive guide analyzes fee structures across major exchanges, hidden costs, optimization strategies, and total cost calculations. You will learn about maker-taker spreads, withdrawal fees, deposit costs, and advanced techniques used by professional traders to minimize exchange expenses.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Crypto Exchange Fee Structures
- Trading Fees: Maker vs Taker Explained
- Major Exchange Fee Comparison 2025
- Deposit and Withdrawal Fees
- Hidden Costs You Must Know
- Exchange Token Fee Discounts
- VIP Programs and Volume Discounts
- Fee Optimization Strategies
- Regional Fee Differences
- DeFi vs CEX Fee Comparison
- Fee Impact on Trading Strategies
- Tax Implications of Exchange Fees
- Future of Exchange Fee Models
- FAQs
- Choose the Right Exchange
Understanding Crypto Exchange Fee Structures
Crypto exchanges generate revenue through multiple fee categories including trading fees, withdrawal charges, deposit costs, and premium services. Fee structures vary significantly between platforms, with some exchanges offering zero-commission trading while monetizing through spreads and other mechanisms.
Modern exchange fee models balance competitive pricing with sustainable business operations. Crypto exchanges like Binance use tiered pricing based on trading volume, while platforms like Coinbase employ simplified flat-rate structures appealing to retail investors.
Primary fee categories include:
- Trading fees: Charged per transaction as percentage of trade value
- Spread costs: Difference between buy and sell prices in market orders
- Withdrawal fees: Fixed or percentage-based charges for moving funds off-platform
- Deposit fees: Costs for funding accounts (rare on major exchanges)
- Premium services: Advanced features, API access, and institutional tools
- Conversion fees: Currency exchange and stablecoin conversion charges
Fee Transparency and Disclosure
Reputable exchanges provide comprehensive fee schedules with clear breakdowns of all charges. Transparent pricing enables traders to calculate total costs accurately and compare platforms effectively.
Key transparency indicators include:
- Detailed fee schedules published prominently on exchange websites
- Real-time fee calculations during trade execution
- Historical fee reporting in account statements
- Clear disclosure of all potential charges and conditions
- Regular updates when fee structures change
Warning signs of poor fee transparency:
- Hidden fees discovered only after transaction completion
- Unclear or missing fee documentation
- Frequent unannounced fee changes
- Complex fee structures without adequate explanation
- Misleading “zero-fee” marketing with undisclosed costs
Trading Fees: Maker vs Taker Explained
Trading fees differentiate between market makers who provide liquidity and takers who consume existing order book liquidity. This maker-taker model encourages order book depth while generating revenue from active trading.
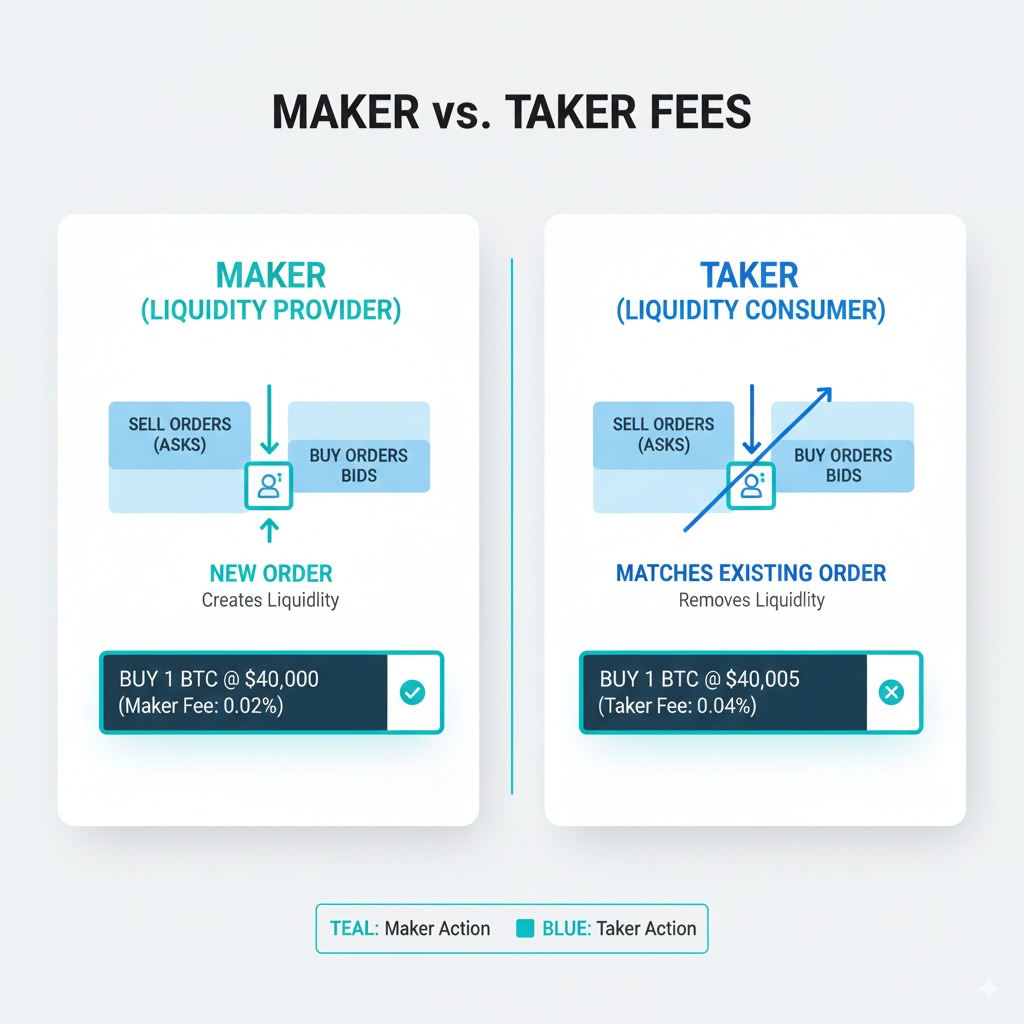
Maker orders add liquidity by placing limit orders that don’t immediately execute against existing orders. Makers receive lower fees or even rebates for providing liquidity that improves trading conditions for other users.
Taker orders remove liquidity through market orders or limit orders that immediately match against existing order book entries. Takers pay higher fees for consuming available liquidity and receiving instant execution.
Maker Fee Benefits and Strategies
Maker fees typically range from 0% to 0.1% across major exchanges, with some platforms offering rebates up to 0.025%. Professional traders optimize for maker status to minimize costs while providing market liquidity.
Maker optimization techniques:
- Use limit orders instead of market orders when possible
- Set orders slightly away from current market price
- Monitor order book depth to identify optimal placement levels
- Utilize post-only order types that guarantee maker status
- Time orders during low-volatility periods for better fill rates
Exchange maker fee examples:
- Binance: 0.02% maker fee (VIP 0), -0.025% rebate (VIP 9)
- Coinbase Pro: 0.00% to 0.50% based on 30-day volume
- Kraken: 0.16% maker fee, declining to 0.00% at highest tiers
- OKX: 0.08% maker fee, with rebates for high-volume traders
Taker Fee Costs and Considerations
Taker fees range from 0.04% to 0.75% depending on exchange and volume tier. While higher than maker fees, taker orders provide guaranteed execution and speed advantages for time-sensitive trades.
When taker fees are justified:
- Urgent trades requiring immediate execution
- Large orders where slippage exceeds fee differences
- Market volatility making limit order fills uncertain
- Futures trading opportunities with time-sensitive windows
- Stop-loss and liquidation scenarios requiring instant execution
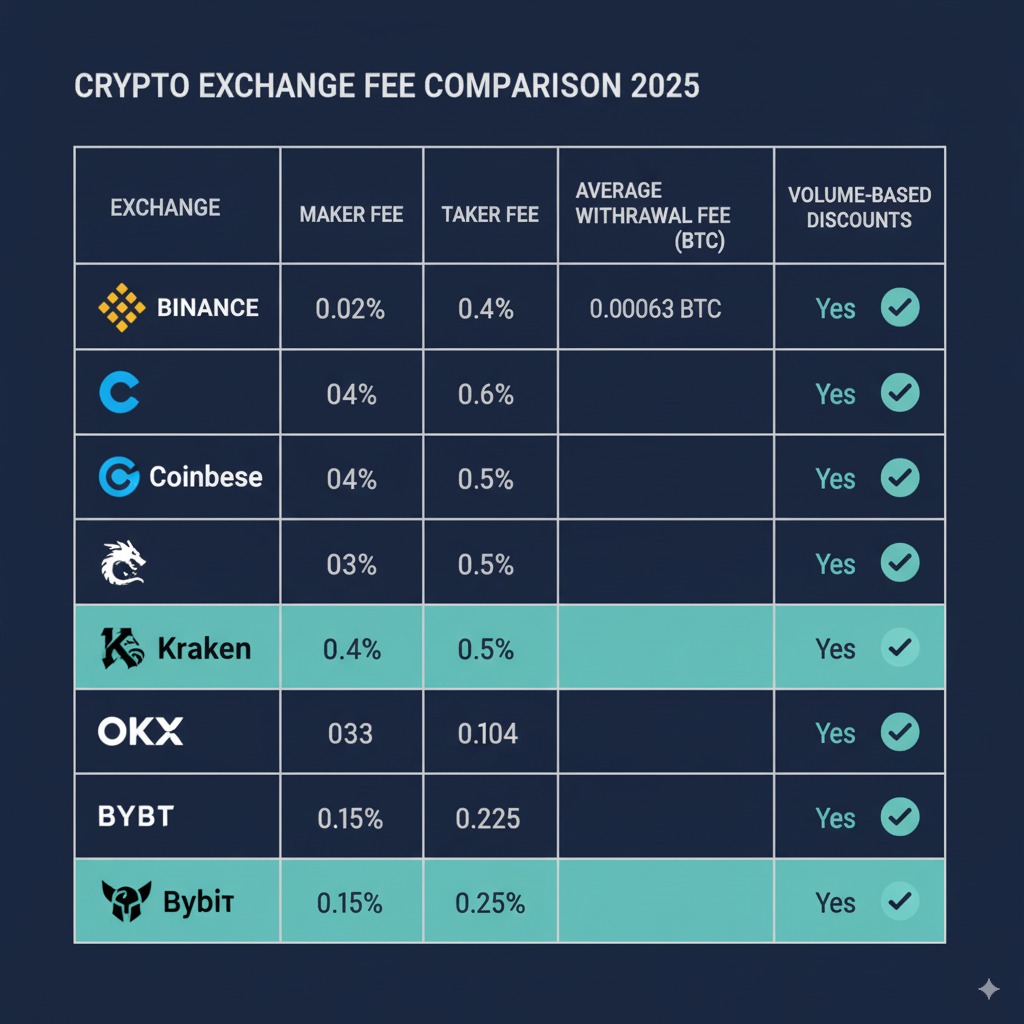
Major Exchange Fee Comparison 2025
Binance Fee Structure
Binance operates the world’s largest crypto exchange with competitive fee rates starting at 0.02% maker and 0.04% taker for VIP 0 users. The platform offers significant fee reductions through BNB token holdings and trading volume increases.
Binance fee tiers (selected levels):
| VIP Level | 30-Day Volume (USDT) | BNB Balance | Maker Fee | Taker Fee |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIP 0 | < 1,000 | Any | 0.020% | 0.040% |
| VIP 1 | ≥ 1,000 | ≥ 25 BNB | 0.018% | 0.036% |
| VIP 2 | ≥ 5,000 | ≥ 25 BNB | 0.016% | 0.032% |
| VIP 4 | ≥ 50,000 | ≥ 250 BNB | 0.012% | 0.024% |
| VIP 9 | ≥ 400,000,000 | ≥ 11,000 BNB | -0.025% | 0.002% |
Binance additional fees:
- Withdrawal fees: Vary by cryptocurrency (0.0005 BTC, 0.005 ETH)
- Deposit fees: Free for most cryptocurrencies
- Convert fees: 0.1% for small amount conversions
- Crypto staking fees: Commission rates for staking services
- Futures fees: 0.02% maker, 0.04% taker (separate from spot)
Coinbase Fee Structure
Coinbase offers different fee structures between Coinbase (retail) and Coinbase Pro (advanced) platforms. The retail platform uses spread-based pricing while Coinbase Pro employs maker-taker fees.
Coinbase Pro fee tiers:
| 30-Day Volume (USD) | Maker Fee | Taker Fee |
|---|---|---|
| $0 – $10,000 | 0.50% | 0.50% |
| $10,000 – $50,000 | 0.35% | 0.35% |
| $50,000 – $100,000 | 0.25% | 0.35% |
| $100,000 – $1,000,000 | 0.15% | 0.25% |
| $1,000,000+ | 0.00% | 0.10% |
Coinbase additional costs:
- Retail spreads: ~0.5% spread on market orders
- Withdrawal fees: Free for most cryptocurrencies
- ACH deposits: Free with 7-day hold period
- Wire transfers: $10 deposit, $25 withdrawal
- Conversion fees: ~2% for retail platform conversions
Kraken Fee Structure
Kraken provides transparent fee pricing with volume-based discounts and maker rebates at higher tiers. The exchange targets both retail and institutional traders with competitive rate structures.
Kraken fee schedule:
| 30-Day Volume (USD) | Maker Fee | Taker Fee |
|---|---|---|
| $0 – $50,000 | 0.16% | 0.26% |
| $50,000 – $100,000 | 0.14% | 0.24% |
| $100,000 – $250,000 | 0.12% | 0.22% |
| $1,000,000 – $2,500,000 | 0.08% | 0.18% |
| $10,000,000+ | 0.00% | 0.10% |
Kraken additional services:
- Withdrawal fees: Competitive rates (0.00015 BTC, 0.0025 ETH)
- Deposit fees: Free for most funding methods
- Margin trading: 0.02% rollover fee every 4 hours
- Futures trading: Separate fee structure for derivatives
OKX and Other Major Exchanges
OKX and other tier-1 exchanges offer competitive fee structures targeting different market segments. Regional exchanges often provide advantages for local users through lower fees or preferred payment methods.
Additional major exchange fees:
| Exchange | Maker Fee | Taker Fee | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| OKX | 0.08% | 0.10% | OKB token discounts |
| Bybit | 0.01% | 0.06% | Derivatives focus |
| KuCoin | 0.02% | 0.04% | KCS token benefits |
| Gate.io | 0.02% | 0.04% | Wide altcoin selection |
| Huobi | 0.20% | 0.20% | HT token discounts |
Deposit and Withdrawal Fees
Cryptocurrency Withdrawal Fees
Withdrawal fees vary significantly between exchanges and cryptocurrencies, representing a major cost factor for active traders. Fees typically reflect network costs plus exchange profit margins, with some platforms charging premium rates.
Common withdrawal fee ranges:
- Bitcoin (BTC): 0.0002 – 0.001 BTC ($4 – $20)
- Ethereum (ETH): 0.003 – 0.01 ETH ($6 – $20)
- USDT (ERC-20): $1 – $25 depending on network congestion
- USDT (TRC-20): $1 – $5 on TRON network
- Binance Smart Chain: $0.10 – $2 for BEP-20 tokens
Fiat Deposit and Withdrawal Costs
Fiat funding methods incur varying fees depending on payment method and geographic location. Wire transfers, ACH payments, and credit cards have different cost structures affecting overall trading economics.
Fiat funding fee comparison:
| Funding Method | Deposit Fee | Withdrawal Fee | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank Transfer (ACH) | Free | Free – $25 | 1-5 business days |
| Wire Transfer | $0 – $15 | $15 – $50 | Same day |
| Credit/Debit Card | 1.5% – 4% | Not available | Instant |
| PayPal | Free – 2% | 1% – 2% | Instant |
| SEPA Transfer | Free | €0.15 – €5 | 1-2 business days |
Network Fee Optimization
Exchanges often charge higher withdrawal fees than actual network costs, creating arbitrage opportunities for cost-conscious traders. Understanding network fee structures helps minimize withdrawal expenses.
Network fee optimization strategies:
- Use lower-cost networks: TRON (TRC-20) vs Ethereum (ERC-20) for USDT
- Batch withdrawals: Combine multiple small withdrawals into larger transactions
- Time network congestion: Withdraw during low-activity periods
- Consider layer-2 solutions: Polygon, Arbitrum for reduced Ethereum fees
- Use exchange internal transfers: Free transfers between accounts on same platform
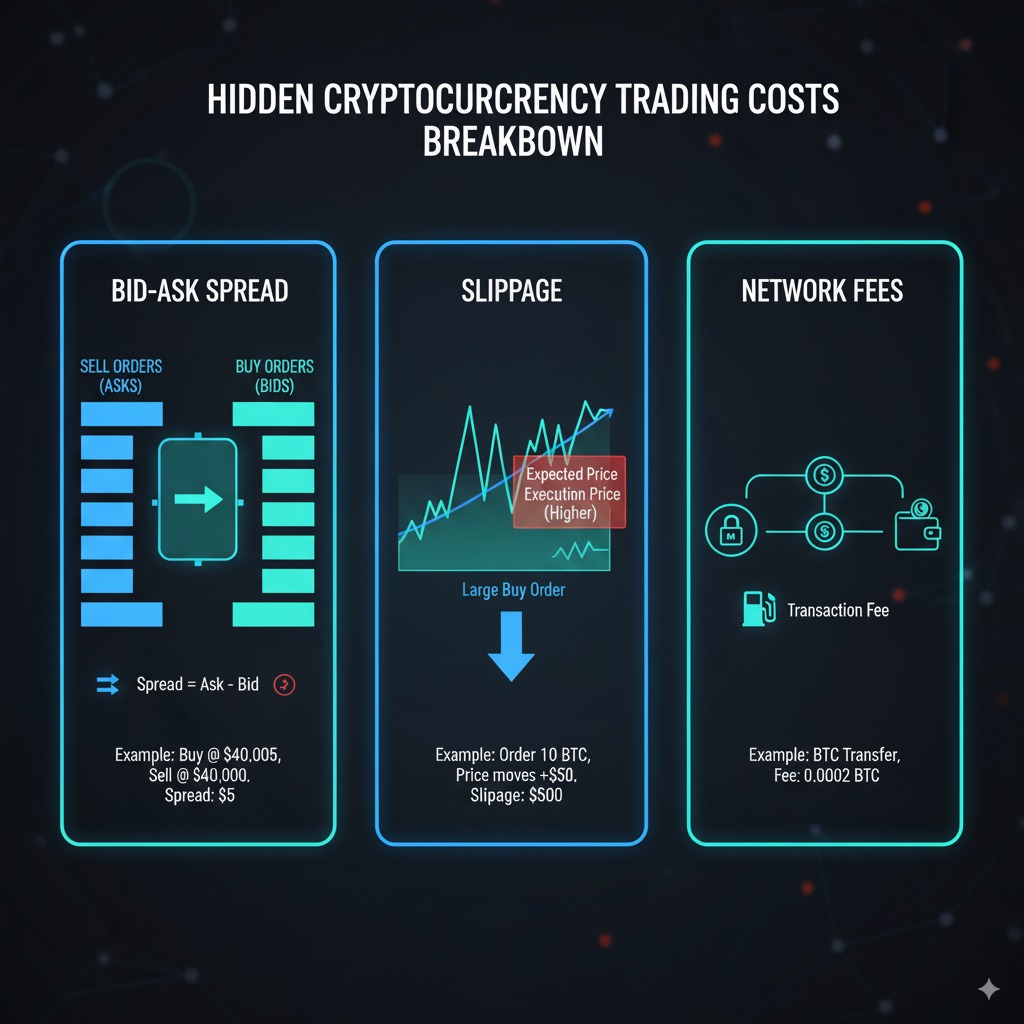
Hidden Costs You Must Know
Spread Costs and Market Impact
Hidden spread costs can exceed visible trading fees, particularly for market orders and low-liquidity trading pairs. The spread represents the difference between highest bid and lowest ask prices, directly impacting trade execution costs.
Spread cost factors:
- Market liquidity: Narrow spreads for major pairs, wide spreads for altcoins
- Order size: Large orders face higher slippage and market impact
- Volatility periods: Spreads widen during high volatility events
- Trading time: Spreads typically wider during off-peak hours
- Exchange selection: Liquidity varies significantly between platforms
Slippage and Price Impact
Slippage occurs when trade execution prices differ from expected prices due to market movement or insufficient liquidity. Large orders particularly suffer from slippage as they consume multiple price levels in the order book.
Slippage mitigation techniques:
- Split large orders: Break significant trades into smaller parcels
- Use limit orders: Set maximum acceptable execution prices
- Time trades strategically: Trade during high-liquidity periods
- Monitor order book depth: Ensure adequate liquidity before trading
- Consider alternative venues: Some exchanges offer better liquidity for specific pairs
Currency Conversion and Cross-Rate Fees
Multi-currency trading incurs conversion fees and unfavorable exchange rates that compound trading costs. Exchanges often markup currency conversion rates above interbank rates while charging additional conversion fees.
Conversion cost examples:
- USD to EUR conversion: 0.5% – 2% markup over mid-market rates
- Stablecoin conversions: 0.1% – 0.5% for USDT/USDC/BUSD swaps
- Fiat to crypto onramp: 1% – 5% depending on payment method
- Cross-trading pairs: Higher fees for non-USD denominated pairs
- Weekend rates: Wider spreads during low-liquidity periods
Exchange Token Fee Discounts
BNB Token Benefits on Binance
Binance Coin (BNB) provides up to 25% fee discounts when used for trading fee payments on Binance. The discount percentage decreases annually but remains significant for active traders.

BNB discount schedule:
- 2024: 12.5% discount when paying fees with BNB
- 2023: 15% discount (reduced from previous years)
- Historical: Started at 50% discount in 2017, reducing by 5% annually
- VIP tiers: Additional discounts based on BNB holdings and trading volume
- Other benefits: Launchpad access, staking rewards, payment applications
Other Exchange Token Programs
Major exchanges offer native tokens providing fee discounts and additional benefits to encourage platform loyalty. Token utility extends beyond fee discounts to governance, staking rewards, and exclusive features.
Exchange token comparison:
| Exchange | Token | Fee Discount | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| OKX | OKB | Up to 30% | Trading competitions, staking |
| KuCoin | KCS | Up to 20% | Daily dividends, bonus programs |
| Huobi | HT | Up to 50% | VIP upgrades, voting rights |
| Gate.io | GT | Up to 25% | Startup participation, voting |
| FTX | FTT | Up to 60% | Reduced spreads, free withdrawals |
Token Holding Strategies
Exchange token investments require careful consideration of price volatility, utility value, and holding requirements. Token prices fluctuate independently of fee savings, potentially offsetting discount benefits.
Token strategy considerations:
- Volatility risk: Token price swings can exceed fee savings
- Minimum holdings: Required balances for discount tiers
- Liquidity needs: Tokens tied up for discounts reduce trading flexibility
- Utility value: Additional benefits beyond fee discounts
- Long-term viability: Exchange success affects token value sustainability
VIP Programs and Volume Discounts
Volume-Based Tier Systems
Exchange VIP programs provide escalating benefits based on 30-day trading volume and platform holdings. Higher tiers unlock lower fees, priority support, and exclusive features valuable for professional traders.
Typical VIP tier progression:
- Entry level: Standard retail fees with basic support
- Low tiers (VIP 1-3): 10-30% fee reductions, faster support response
- Mid tiers (VIP 4-6): 40-60% fee reductions, dedicated account managers
- High tiers (VIP 7-9): Maximum discounts, institutional-level services
- Institutional: Custom arrangements, API rate limits, special rates
Qualification Requirements
VIP tier qualification combines trading volume metrics with platform token holdings. Requirements scale exponentially at higher levels, targeting institutional and whale traders.
Common qualification metrics:
- 30-day trading volume: Primary determinant for tier advancement
- Platform token holdings: Secondary requirement for fee discounts
- Account balance: Some exchanges require minimum asset holdings
- Trading consistency: Regular activity maintains tier status
- Geographic restrictions: VIP benefits may vary by jurisdiction
Professional Trading Benefits
High-tier VIP programs offer institutional-grade services including dedicated support, custom API limits, and preferential treatment. These benefits provide operational advantages beyond fee savings for serious traders.
Advanced VIP benefits:
- Dedicated account management: Personal relationship managers
- Custom API limits: Higher request rates and priority processing
- Early access: New features and trading pairs before general release
- Research reports: Institutional-quality market analysis and insights
- Event access: Exclusive webinars, conferences, and networking opportunities
Fee Optimization Strategies
Trading Pattern Optimization
Strategic trading pattern adjustments can reduce fees by 30-50% without changing investment strategy fundamentals. Professional traders systematically optimize execution methods to minimize costs while maintaining performance.
Optimization techniques:
- Maker order preference: Use limit orders instead of market orders when possible
- Volume concentration: Focus trading on single exchange to achieve VIP tiers
- Token utilization: Maintain exchange tokens for fee discounts
- Timing optimization: Trade during high-liquidity periods for better spreads
- Order splitting: Break large orders to minimize market impact
Multi-Exchange Arbitrage
Advanced traders utilize multiple exchanges to optimize costs and execution quality. Different exchanges excel in various aspects including fees, liquidity, and asset availability.
Multi-exchange strategies:
- Fee comparison shopping: Route trades to lowest-cost venues
- Liquidity optimization: Use exchanges with deepest order books for large trades
- Geographic arbitrage: Access region-specific exchanges with lower fees
- Token-specific venues: Use exchanges specializing in particular cryptocurrencies
- Security considerations: Balance cost savings with platform safety
Portfolio-Level Cost Management
Comprehensive fee management requires portfolio-level optimization considering all trading activities and associated costs. Total cost analysis includes direct fees, hidden costs, and opportunity costs.
Portfolio optimization approaches:
- Trading frequency analysis: Reduce unnecessary trades that only generate fees
- Asset allocation efficiency: Minimize rebalancing frequency and associated costs
- Tax-loss harvesting: Coordinate fee optimization with tax efficiency strategies
- Liquidity management: Maintain cash positions to avoid forced liquidations
- Platform consolidation: Reduce complexity while maintaining competitive execution
Regional Fee Differences
Geographic Fee Variations
Exchange fees vary significantly by geographic region due to regulatory requirements, local competition, and operational costs. Understanding regional differences helps optimize platform selection for international traders.
Regional fee patterns:
- United States: Higher fees due to regulatory compliance costs
- European Union: Moderate fees with strong consumer protection
- Asia-Pacific: Competitive fees with high-volume retail markets
- Emerging markets: Variable fees depending on local banking infrastructure
- Tax havens: Potentially lower fees but regulatory uncertainties
Regulatory Impact on Costs
Regulatory compliance requirements directly impact exchange operating costs and fee structures. Jurisdictions with stricter oversight typically correlate with higher trading fees and service charges.
Regulatory cost factors:
- Licensing fees: Regulatory approval and ongoing compliance costs
- Reporting requirements: Transaction monitoring and suspicious activity reporting
- Consumer protection: Insurance requirements and segregated customer funds
- Tax withholding: Automatic tax deduction and reporting obligations
- Anti-money laundering: KYC verification and ongoing customer monitoring
Currency-Specific Considerations
Local currency support and payment methods significantly affect total trading costs. Exchanges offering native currency support typically provide better rates and lower conversion fees for domestic users.
Currency optimization factors:
- Native banking integration: Direct bank transfers vs international wires
- Local payment methods: Regional payment systems with lower costs
- Currency conversion rates: Domestic vs international exchange rate markups
- Settlement times: Faster local processing vs international delays
- Regulatory familiarity: Understanding local compliance requirements
DeFi vs CEX Fee Comparison
Decentralized Exchange Costs
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) eliminate traditional trading fees while introducing network gas costs and liquidity provider spreads. Total DEX costs vary significantly based on network congestion and trade size.
DEX cost components:
- Network gas fees: Variable costs based on blockchain congestion
- Liquidity provider fees: Typically 0.05% – 1% depending on pool
- Slippage costs: Price impact for trades in automated market makers
- MEV costs: Maximal extractable value affecting trade execution
- Bridge fees: Cross-chain transaction costs for multi-chain DEXs
Centralized vs Decentralized Trade-offs
Cost comparison between CEXs and DEXs requires comprehensive analysis including direct fees, hidden costs, and operational complexities. Neither model consistently provides lower costs across all scenarios.
CEX advantages:
- Predictable fees: Fixed percentage rates with clear disclosure
- Deep liquidity: Narrow spreads for major trading pairs
- Advanced orders: Stop-losses, limit orders without additional network costs
- Fiat integration: Direct bank transfers and credit card processing
- Customer support: Human assistance for technical issues
DEX advantages:
- No platform fees: Eliminate exchange profit margins from trading costs
- Direct custody: Maintain control of private keys throughout trading
- Censorship resistance: No geographic restrictions or account limitations
- Liquidity mining: Earn additional rewards through yield farming
- Innovation access: Early access to new tokens and protocols
Fee Impact on Trading Strategies
High-Frequency Trading Considerations
High-frequency and algorithmic trading strategies require ultra-low fees to maintain profitability. Small fee differences compound significantly across thousands of trades, making fee optimization critical for systematic strategies.
HFT fee optimization:
- Maker rebates: Prioritize exchanges offering negative fees for liquidity provision
- API efficiency: Minimize round-trip times to reduce slippage costs
- Colocation services: Physical proximity to exchange servers for speed advantages
- Volume negotiations: Custom fee arrangements for substantial trading volume
- Cross-venue arbitrage: Exploit fee differences between platforms
Long-Term Investment Impact
Even buy-and-hold strategies benefit from fee optimization, particularly during portfolio rebalancing and dollar-cost averaging programs. Compound effects of fee savings significantly impact long-term wealth accumulation.
Long-term optimization strategies:
- Rebalancing frequency: Balance portfolio drift against rebalancing costs
- Dollar-cost averaging: Batch purchases to reduce per-transaction costs
- Platform loyalty: Achieve VIP tiers through concentrated activity over time
- Token holdings: Maintain exchange tokens for ongoing fee discounts
- Tax coordination: Consider fee deductibility in tax planning strategies
Risk Management Costs
Risk management activities including stop-losses, hedging, and portfolio protection incur additional fees that must be factored into overall strategy costs. Effective risk management balances protection benefits against implementation costs.
Risk management fee considerations:
- Stop-loss orders: Market order execution during volatility periods
- Options hedging: Premium costs and exercise fees for downside protection
- Futures hedging: Rolling costs and basis risk management
- Diversification trades: Costs of maintaining balanced portfolio allocations
- Emergency liquidity: Premium costs for urgent position adjustments
Tax Implications of Exchange Fees
Fee Deductibility Rules
Exchange fees may qualify as tax-deductible business expenses for professional traders in many jurisdictions. Proper documentation and classification enable significant tax savings for active trading operations.
Deductible fee categories:
- Trading fees: Direct costs of buying and selling securities
- Platform subscriptions: Professional trading tools and data services
- Research costs: Market analysis and professional advisory services
- Technology expenses: API access and algorithmic trading infrastructure
- Education costs: Trading courses and professional development
Record-Keeping Requirements
Accurate fee tracking requires comprehensive records supporting tax deduction claims and cost basis calculations. Professional tax preparation may justify costs through improved deduction optimization.
Essential documentation:
- Transaction records: Complete history of all trades and associated fees
- Platform statements: Monthly and annual summaries from all exchanges
- Fee categorization: Separation of trading vs investment vs business expenses
- Foreign exchange rates: Currency conversion documentation for international trades
- Professional expenses: Documentation of trading-related business costs
International Tax Considerations
Cross-border trading activities create complex tax situations requiring professional guidance for compliance optimization. Fee deductibility rules vary significantly between tax jurisdictions.
International tax factors:
- Withholding taxes: Foreign exchange fee withholding and credit claiming
- Transfer pricing: Related party transaction documentation for businesses
- Treaty benefits: Double taxation avoidance through bilateral agreements
- Reporting requirements: Foreign account and transaction disclosure obligations
- Currency translations: Consistent foreign exchange rate methodologies
Future of Exchange Fee Models
Zero-Fee Trading Trends
Commission-free trading models continue expanding as exchanges seek alternative revenue sources. Payment for order flow, spread monetization, and premium services replace traditional trading fee revenues.
Alternative monetization methods:
- Payment for order flow: Revenue from market makers for trade routing
- Premium subscriptions: Advanced features and professional tools
- Lending services: Interest income from margin and spot lending
- Staking rewards: Commission from proof-of-stake delegation services
- NFT and gaming: Revenue from digital asset and gaming platforms
Regulatory Standardization
Regulatory harmonization efforts may standardize fee disclosure and structure requirements across jurisdictions. Increased transparency benefits consumers while potentially raising compliance costs.
Regulatory trends:
- Fee transparency: Mandatory disclosure of all costs and revenue sources
- Best execution: Requirements to provide optimal trade execution for customers
- Consumer protection: Standardized dispute resolution and compensation mechanisms
- Market structure: Rules governing market making and liquidity provision
- Cross-border coordination: International cooperation on regulatory frameworks
Technology Innovation Impact
Blockchain technology and layer-2 scaling solutions continue reducing infrastructure costs, potentially enabling lower exchange fees. Lightning Network, Polygon, and other solutions decrease operational expenses.
Technology-driven cost reductions:
- Layer-2 scaling: Reduced network costs for blockchain interactions
- Automated market making: Algorithmic liquidity provision reducing operational costs
- Cross-chain protocols: Improved interoperability reducing bridge fees
- Central bank digital currencies: Direct integration reducing fiat conversion costs
- Artificial intelligence: Automated customer service and risk management
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the typical crypto exchange fees?
Most crypto exchanges charge 0.02% to 0.75% per trade, with maker fees typically lower than taker fees. Binance offers 0.02%/0.04% maker/taker rates, while Coinbase charges 0.35% to 0.50% for most retail traders.
How can I reduce crypto trading fees?
Reduce fees through maker order placement, exchange token holdings, volume-based VIP tiers, and platform optimization. Using limit orders instead of market orders can cut fees by 50%, while maintaining exchange tokens provides 10-25% additional discounts.
Are withdrawal fees the same across all exchanges?
No, withdrawal fees vary significantly between exchanges and can differ by 300-500% for the same cryptocurrency. Always compare withdrawal costs before selecting an exchange, especially for frequent withdrawals.
Do DeFi platforms have lower fees than centralized exchanges?
DeFi fees depend on network congestion and can be higher or lower than CEX fees. Ethereum-based DEXs often have higher total costs due to gas fees, while other blockchains like Polygon offer lower-cost alternatives.
How do VIP programs affect trading costs?
VIP programs can reduce trading fees by 50-90% for high-volume traders. Requirements typically start at $50,000+ monthly volume, with the highest tiers requiring millions in trading activity and platform token holdings.
Are exchange fees tax deductible?
Exchange fees may be deductible as business expenses for professional traders or investment expenses for investors, depending on jurisdiction and tax situation. Consult tax professionals for specific guidance on deductibility rules.
Which exchange has the lowest fees overall?
No single exchange has the lowest fees for all users and trading patterns. Binance generally offers competitive rates for most users, while specialized platforms may be optimal for specific use cases.
How do spreads affect total trading costs?
Spreads can exceed visible trading fees, especially for market orders and low-liquidity pairs. Always consider bid-ask spreads when calculating total transaction costs, particularly for large orders.
Do fees differ for different cryptocurrencies?
Yes, fees often vary by trading pair and cryptocurrency. Major pairs like BTC/USDT typically have the lowest fees, while exotic altcoin pairs may have higher charges and wider spreads.
How often do exchanges change their fee structures?
Exchanges typically update fee structures 1-2 times per year, usually with advance notice. Major changes require 30+ days notification, while minor adjustments may have shorter notice periods.
Choose the Right Exchange
Select crypto exchanges based on your trading patterns, volume levels, and geographic location to minimize total costs. The optimal platform varies significantly between casual investors, active traders, and institutional participants.
For beginners and low-volume traders:
- Coinbase: Simple interface, regulatory compliance, educational resources
- Kraken: Transparent fees, strong security, comprehensive support
- Gemini: Regulated platform, insurance coverage, beginner-friendly features
For active traders and higher volumes:
- Binance: Lowest fees, extensive features, global liquidity
- OKX: Competitive rates, derivatives trading, advanced tools
- Bybit: Derivatives focus, maker rebates, professional interface
For institutional and professional trading:
- Binance Institutional: Custom arrangements, dedicated support, API flexibility
- Coinbase Prime: Regulated institutional services, custody integration
- Kraken Pro: Professional tools, high-volume discounts, compliance support
Key selection factors:
- Total cost analysis: Include all fees, spreads, and hidden costs
- Regulatory compliance: Choose licensed platforms in your jurisdiction
- Security standards: Prioritize exchanges with proven security track records
- Liquidity depth: Ensure adequate order book depth for your trading size
- Product availability: Verify access to required trading pairs and features
Action steps to optimize exchange costs:
- Calculate current costs: Analyze your trading patterns and total fee expenses
- Compare alternatives: Evaluate 3-5 platforms based on your usage patterns
- Test platforms: Start with small amounts to verify execution quality
- Optimize features: Implement maker orders, VIP tiers, and token discounts
- Monitor performance: Track costs monthly and adjust strategies as needed
Remember: The cheapest exchange isn’t always the best choice when considering security, liquidity, and regulatory compliance. Balance cost optimization with platform quality and risk management for optimal long-term results.
Ready to reduce your crypto trading costs? Start with Binance for competitive fees and comprehensive trading features, or explore Coinbase for regulated US trading with transparent pricing.
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves substantial risk of loss and may not be suitable for all investors. Exchange fees are subject to change without notice. Past performance does not indicate future results.
Risk Warning: Always verify current fee structures directly with exchanges before trading. Fee optimization strategies may involve additional risks including platform concentration and token volatility.
Educational Purpose: This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment, financial, or tax advice. Consult qualified professionals before making investment decisions regarding exchange selection and fee optimization strategies.
