Coinbase Exchange Explained: Complete 2025 Trading Guide
Coinbase Exchange is the largest U.S.-based cryptocurrency exchange, serving over 110 million users across 100+ countries with more than 250 digital assets available for trading. Founded in 2012 by Brian Armstrong and Fred Ehrsam, Coinbase has evolved from a simple Bitcoin wallet into a comprehensive crypto ecosystem offering spot trading, advanced trading features, staking, NFT marketplace, and institutional services.
Coinbase maintains a 24-hour trading volume exceeding $4 billion and ranks as the #3 cryptocurrency exchange globally by trading volume. The platform combines regulatory compliance with user-friendly design, making it particularly attractive for beginners entering the crypto space while offering advanced tools for experienced traders.
This comprehensive guide explores Coinbase’s core features, trading platforms, fee structure, security measures, and how it compares to other leading exchanges in 2025. You will learn about Coinbase’s regulatory compliance, available cryptocurrencies, advanced trading tools, and practical tips to optimize your trading experience on the platform.
What Is Coinbase Exchange?
Coinbase is one of the top cryptocurrency exchanges that started in 2012, created to make trading Bitcoin easy for everyone. The platform operates as a centralized exchange (CEX), providing a bridge between traditional finance and digital assets through its regulated infrastructure.
Core Business Model: Coinbase functions as both a cryptocurrency exchange and a digital asset custody platform. Users can buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies while the exchange maintains custody of their digital assets in secure storage systems.
Regulatory Standing: As a Nasdaq-listed company, Coinbase follows strict financial regulations, with licensing across the US, UK, and Europe. The platform is registered with FinCEN as a Money Services Business and maintains licenses for money transmission across multiple U.S. jurisdictions.
Geographic Availability: The exchange operates in over 100 countries, though certain features may be restricted based on local regulations. Advanced trading features like derivatives are limited in specific jurisdictions such as the UK.
History and Founding of Coinbase
2012 Foundation: Coinbase was founded by Brian Armstrong, a former Airbnb engineer, and Fred Ehrsam, a former Goldman Sachs trader. The company emerged during Bitcoin’s early adoption phase, positioning itself as a user-friendly gateway to cryptocurrency investing.
Leadership Background: Brian Armstrong serves as CEO, bringing his software engineering expertise from IBM and Airbnb. His educational background includes a bachelor’s degree in economics and computer science from Rice University, plus a master’s degree in computer science.
2021 Public Listing: In April 2021, Coinbase became a publicly traded company through a direct listing on the Nasdaq (COIN), marking a significant milestone in the cryptocurrency industry’s mainstream acceptance. This public status requires quarterly financial reporting and independent audits, enhancing transparency.
Evolution Timeline: The platform evolved from a simple Bitcoin wallet to a comprehensive crypto ecosystem, adding features like Coinbase Pro (now Advanced Trade), institutional services, NFT marketplace, and decentralized finance integrations.
Coinbase Trading Platforms Breakdown
Coinbase offers multiple trading interfaces designed for different user experience levels, from complete beginners to professional traders.
Standard Coinbase Platform
The primary Coinbase interface targets new cryptocurrency investors with its simplified design and instant purchase options.
User Interface: The original Coinbase platform is a relatively simple interface that allows users to purchase cryptocurrency with U.S. dollars. The platform features a clean dashboard with prominent buy/sell buttons and portfolio tracking.
Trading Features: Users can execute instant purchases using debit cards, bank transfers, or PayPal. The platform includes basic portfolio management, price alerts, and educational content through Coinbase Earn.
Target Audience: Designed for beginners who want straightforward crypto purchases without complex trading tools or advanced order types.
Coinbase Advanced Trade
Coinbase Advanced Trade, formerly Coinbase Pro, is designed for active and experienced traders who need access to advanced tools, lower fees, and enhanced charting capabilities.
Advanced Features: Advanced Trade offers over 552 spot trading pairs, including 237 USDC pairs and 22 stable pairs, with advanced charting powered by TradingView. The platform includes limit orders, stop orders, and market orders for precise trade execution.
Fee Structure: Advanced Trade utilizes a maker-taker fee model with significantly lower costs compared to the standard platform. Fees range from 0.00% to 0.40% for maker fees, and 0.05% to 0.60% for taker fees, depending on the total USD trailing 30-day trading volume.
Professional Tools**: TradingView integration provides access to 400+ indicators, 100,000+ public scripts, and real-time chart trading for spot and futures markets.
Coinbase International Exchange
The international platform caters to non-U.S. institutional clients with derivatives trading capabilities.
Derivatives Trading: Users can trade more than 150 perpetual and futures contracts, with U.S. traders having access to commodity contracts and Coinbase 50 Index perpetual futures.
Margin Trading: While Coinbase disabled margin trading in the U.S. due to CFTC guidelines, margin trading remains available on the International Exchange for non-US institutions in select jurisdictions.
24/7 Futures Trading: Coinbase recently launched 24/7 trading for Bitcoin and Ethereum futures, making it the first CFTC-regulated exchange to do so.
Coinbase Fee Structure Comprehensive Analysis
Understanding Coinbase’s fee structure is crucial for optimizing trading costs across different platforms and payment methods.
Standard Platform Fees
Coinbase’s standard platform charges some of the highest fees in the industry, with a 0.50% spread per transaction plus flat fees ranging from $0.99 for trades up to $10, $1.49 for $10–$25, $1.99 for $25–$50, and $2.99 for $50–$200.
Payment Method Impact: Debit card transactions cost 3.99%, PayPal deposits cost 2.5%, while ACH transfers are free but slower due to settlement time. The choice of payment method significantly affects overall trading costs.
Spread Fees: Coinbase charges a spread of 0.50% to 2%, which is built into the quoted price, meaning you pay slightly more than the actual market rate.
Advanced Trade Fee Schedule
The Advanced Trade platform offers substantially lower fees through its volume-based maker-taker model.
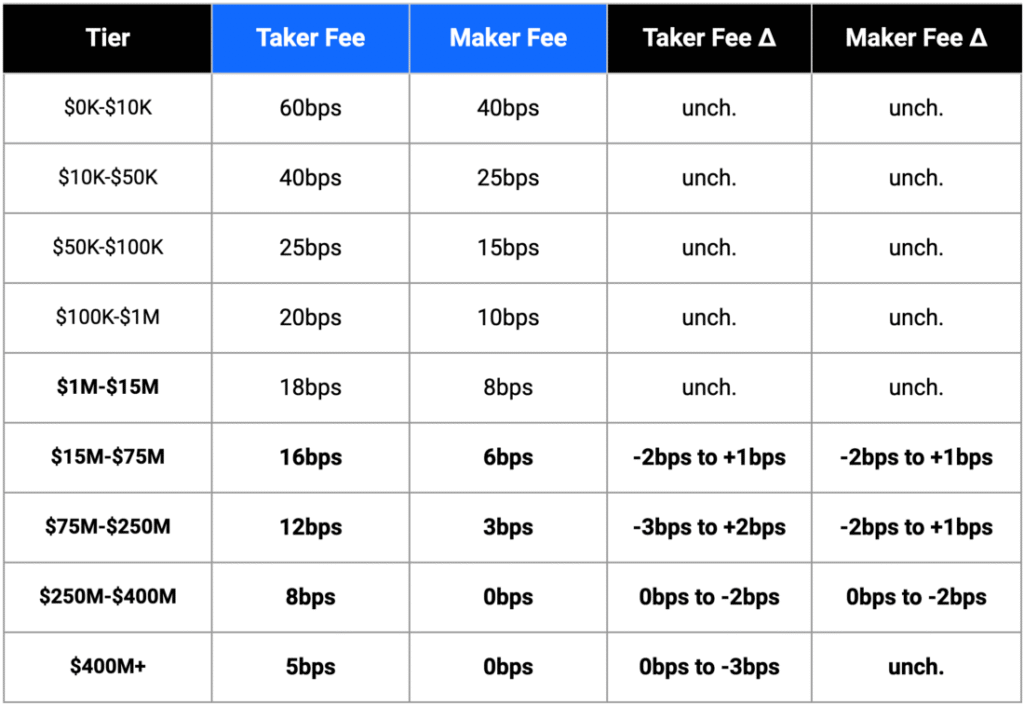
Volume-Based Pricing: For traders with under $1,000 monthly volume, rates start at 0.60% for makers and 1.20% for takers, with fees decreasing as trading volume increases.
High-Volume Benefits: To reach the first Advanced trading fees tier, you need to trade over $10,000 monthly or maintain a $1 million asset balance.
Stable Pair Discounts: Stable pairs (stablecoin trading pairs) have fixed maker fees of 0.00% and taker fees of 0.001%.
Coinbase One Subscription Benefits
Coinbase One costs $29.99/month and provides zero trading fees on hundreds of assets (spread still applies), 25% rebate on Advanced Trade spot fees, and enhanced staking rewards.
Tiered Memberships: Coinbase One now offers three tiers: Basic ($4.99/month), with benefits varying by trading volume limits – Basic users get zero fees on $500 worth of trades monthly, while Preferred users get zero fees on up to $10,000 monthly.
Supported Cryptocurrencies and Trading Pairs
Coinbase maintains one of the largest cryptocurrency selections among U.S. exchanges, with continuous additions and delistings based on regulatory compliance.
Available Digital Assets
Coinbase supports trading for over 250 cryptocurrencies, including major assets like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Solana (SOL), Cardano (ADA), and many altcoins across various sectors like DeFi, NFTs, meme coins, and AI tokens.
Trading Pairs: The platform offers more than 350 crypto-to-crypto trading pairs, enabling diverse trading strategies and portfolio diversification.
Asset Categories: The platform features cryptocurrencies from multiple sectors including:
- Layer 1 blockchains (Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana)
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) protocols
- Non-fungible token (NFT) platforms
- Metaverse and gaming tokens
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning projects
Listing and Delisting Process
Coinbase maintains strict listing criteria based on regulatory compliance, technical security, and market demand. The exchange has delisted tokens like XRP due to regulatory pressure, which drew criticism from users.
Coinbase Effect: The platform’s popularity has led to the ‘Coinbase effect,’ where cryptocurrencies see significant price surges following their listing on the exchange.
Security Features and Asset Protection
Security remains paramount for Coinbase’s operations, with multiple layers of protection for user funds and personal information.
Cold Storage and Custody
Coinbase uses strong security measures, keeping 98% of funds in offline cold storage, along with insurance coverage and two-factor authentication for accounts.
Multi-Signature Wallets: The platform stores the majority of user funds in offline multi-signature crypto wallets, requiring multiple cryptographic signatures for fund access.
Coinbase Vault: For additional security, Coinbase offers Coinbase Vault, which enables time-delayed withdrawals and multi-signature approvals.
Insurance and Regulatory Compliance
Coinbase provides FDIC insurance for USD balances up to $250,000 and maintains comprehensive security features including two-factor authentication (2FA).
Regulatory Licenses: The platform holds licenses from trusted regulators including the US New York State Department of Financial Services, UK Financial Conduct Authority, and Central Bank of Ireland.
Recent Security Incidents
Coinbase faced a hacking attack in May 2025 where attackers gained access to names, addresses, phone numbers, emails, government identification documents, balance snapshots, and transaction histories of users. However, the company handled the incident transparently and notified affected users promptly.
Coinbase Additional Services and Features
Beyond basic trading, Coinbase offers a comprehensive ecosystem of crypto-related services.
Staking and Earn Programs
Coinbase’s staking program offers potential APY up to 12% on nine different coins that can earn rewards. The platform handles technical staking requirements while users earn passive income.
Coinbase Earn: The platform provides a “learn while you earn” program with video classes and exams that educate users about cryptocurrency trading, rewarding completion with small amounts of featured cryptocurrencies.
Coinbase Card and Payment Solutions
Coinbase Card functions as a Visa debit card that converts cryptocurrency assets to money for daily expenses. The card enables real-world spending of crypto holdings while earning rewards.
Payment Methods: Coinbase supports various payment methods including debit cards, bank accounts (ACH), PayPal, and mobile wallets (Apple Pay and Google Pay) for U.S. customers.
Coinbase Wallet and DeFi Access
Coinbase Wallet is an independent self-custody wallet service accessible without registering on Coinbase.com, supporting EVM and Solana-compatible networks through browser extensions and mobile apps.
DeFi Integration: The wallet includes decentralized exchange (DEX) functionality and supports interaction with decentralized applications across multiple blockchain networks.
User Experience and Mobile Applications
Coinbase prioritizes user experience across both web and mobile platforms, with interfaces designed for different skill levels.
[INSERT IMAGE: Screenshots of Coinbase mobile app interface showing trading dashboard and portfolio view]
Mobile App Features
The Coinbase mobile app (available on iOS and Android) allows users to trade crypto anytime, anywhere, with an intuitive interface and clean dashboard providing quick access to buying, selling, and receiving crypto.
Security Features: The app includes biometric logins, two-factor authentication, and secure transaction confirmations for enhanced mobile security.
Customer Support
Coinbase includes an extensive help center with FAQs, guides, and automated assistance, with premium services like Coinbase One including 24/7 priority support.
Support Challenges: However, Coinbase has faced criticism for its support, with many customers complaining about receiving automated responses instead of personalized solutions, and over 1,000 cases reported to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau in one year.
Getting Started with Coinbase
Creating a Coinbase account involves several verification steps due to regulatory requirements.
Account Registration Process
The Coinbase sign-up process is quick and straightforward, requiring users to enter an email address and password, then verify their account using a code sent to their phone number or email.
KYC Verification: Coinbase is a KYC exchange, requiring customers to send identification documents like a driver’s license or passport. This process ensures compliance with anti-money laundering regulations.
Account Verification: Once created, users must complete Know-Your-Customer (KYC) verification and provide details about their financial status.
First Trade Execution
New users can purchase as little as $1 of Bitcoin on Coinbase, though this comes with a $0.50 fee, netting approximately $0.50 of actual Bitcoin. This low minimum allows beginners to start with minimal risk.
Coinbase vs Competitors Comparison
Understanding how Coinbase compares to other major exchanges helps inform platform selection decisions.
Fee Comparison
While Coinbase charges notably higher fees than many exchanges, Kraken provides a compelling alternative with trading fees starting at 0.26% for market orders and rates as low as 0% for increased trading volume.
Alternative Platforms: Exchanges like Binance, Bybit, OKX, Bitget, and Gate.io offer lower fees, tighter spreads, and equally strong security, potentially ensuring greater long-term profitability.
[INSERT IMAGE: Comparison chart showing Coinbase fees vs competitors like Binance, Bybit, OKX with percentage rates]
Regulatory Advantages
As a NASDAQ-listed exchange, Coinbase follows tier-1 compliance standards, prioritizing regulation, security, and ease of use, which translates to higher spreads and fees but enhanced user protection.
User Base and Adoption
Coinbase serves more than 110 million people from over 100 countries, making it one of the largest cryptocurrency platforms globally by user count.
Coinbase Limitations and Considerations
While Coinbase offers numerous advantages, several limitations should be considered before choosing the platform.
High Fee Structure
Coinbase fees can be confusing and higher than competitors, with less transparency than previously offered. The platform’s emphasis on regulatory compliance and user experience comes at the cost of higher trading fees.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The company faces legal uncertainty as the SEC accuses it of breaking securities rules. This ongoing regulatory scrutiny may impact future service offerings and compliance requirements.
Geographic Restrictions
Derivatives trading and other advanced features are restricted in certain countries, such as the UK. Users should verify available features in their jurisdiction before account creation.
Future of Coinbase Exchange
Coinbase continues evolving its platform through technological innovations and service expansions.
Recent Developments
2025 saw Coinbase Advanced expand its offering with new futures products including Natural Gas (NGS) futures with up to 11x leverage and Cardano (ADA) futures with up to 5x leverage.
Technology Integration
The platform’s integration with TradingView and expansion of derivative products demonstrates Coinbase’s commitment to serving advanced traders while maintaining accessibility for beginners.
Regulatory Leadership
Coinbase has been exceptionally proactive and cooperative in seeking a well-defined regulatory framework for crypto businesses in the U.S., positioning itself as a leader in compliance and industry standards.
Conclusion
Coinbase Exchange stands as the largest U.S.-based cryptocurrency platform, offering a comprehensive suite of trading services from basic cryptocurrency purchases to advanced derivatives trading. While the platform charges higher fees compared to some competitors, its regulatory compliance, user-friendly interface, and extensive security measures make it particularly attractive for beginners and institutional investors prioritizing safety and reliability.
The platform’s evolution from a simple Bitcoin wallet to a publicly-traded financial services company demonstrates its commitment to mainstream cryptocurrency adoption. However, users should carefully consider fee structures and geographic restrictions when choosing Coinbase for their trading needs.
For those prioritizing ease of use, regulatory compliance, and comprehensive customer support, Coinbase represents a solid choice despite higher costs. Advanced traders seeking lower fees may benefit from using Coinbase Advanced Trade or exploring alternative platforms like those featured in our comprehensive crypto exchange comparison guide.
Ready to start trading on Coinbase? Remember to begin with small amounts, utilize Advanced Trade for lower fees, and take advantage of educational resources to maximize your cryptocurrency trading success.
