Bitcoin Futures Trading Guide (2025)
Direct answer: Bitcoin futures trading uses standardized contracts to speculate on or hedge the future price of BTC with leverage, enabling strategies like carry (basis), trend, mean-reversion, and hedging driven by funding rates, open interest, liquidations, and options flow. This guide shows you exactly how to read those signals, structure positions, and manage risk like a pro.
Quick Start: Choose a regulated, liquid exchange with deep BTC futures books, transparent funding, and robust risk tools. Compare fees, maker/taker rebates, and maximum leverage.
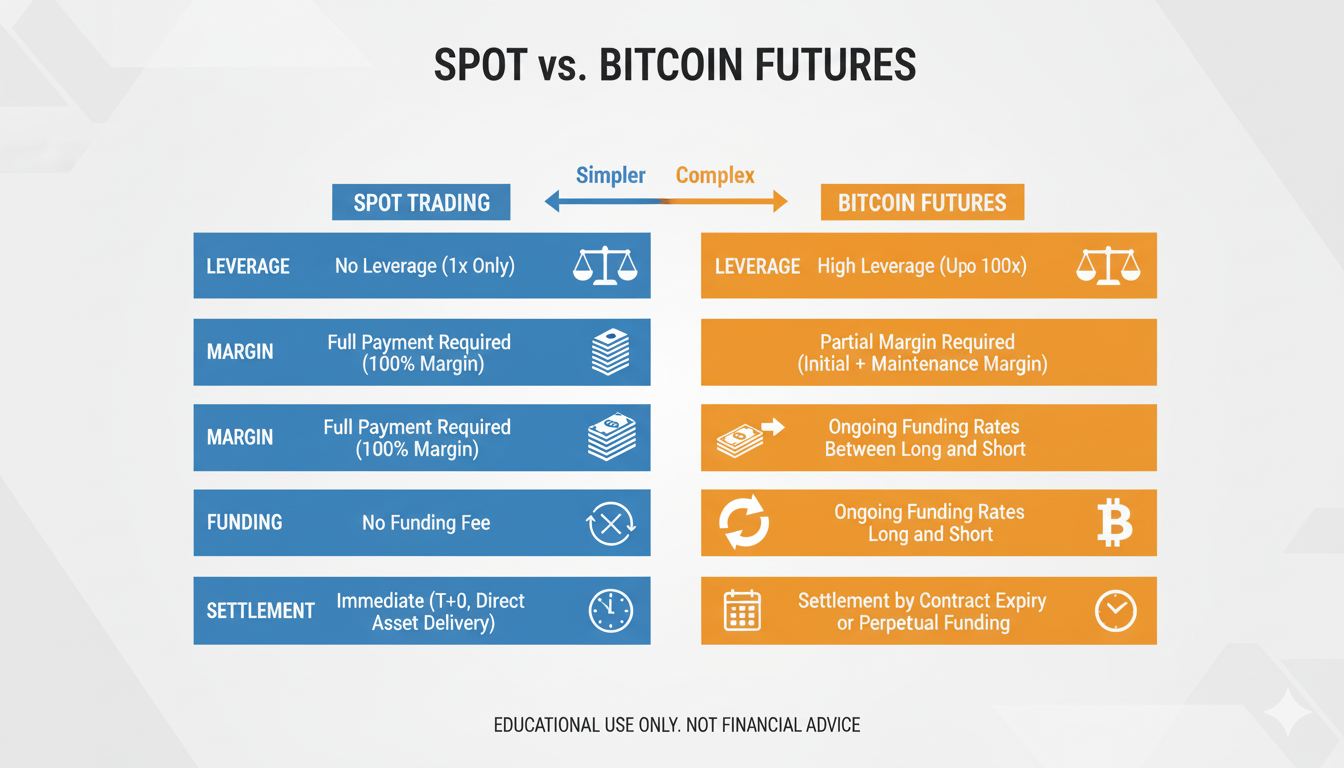
What Is Bitcoin Futures Trading?
Bitcoin futures are derivative contracts that lock in a future Bitcoin price for settlement on a specified date (quarterly) or continuously (perpetual swaps). You trade price direction without owning BTC, using margin and leverage to amplify gains and losses.
How Bitcoin Futures Work vs. Spot
- Spot: Buy/sell BTC instantly; ownership transfers to your wallet/exchange balance.
- Quarterly Futures: Expire on a set date; often trade at a premium/discount (basis) to spot.
- Perpetual Swaps: No expiry; funding rate every 8 hours (varies by venue) aligns perp price with spot.
Why Futures Matter (Hedging, Leverage, Speculation)
- Hedging: Lock in USD value of holdings by shorting futures.
- Leverage: Control larger notional with smaller margin; manage risk tightly.
- Strategy Breadth: Basis carry, calendar spreads, breakout/mean-reversion, news/macro plays.
Where to Trade BTC Futures
Choose high-liquidity venues with deep books and risk controls.
Key Market Drivers of Bitcoin Futures
Open Interest, Funding Rates, and Liquidations
Open Interest (OI): Total outstanding contracts. Rising OI with rising price signals leverage build; steep OI into resistance increases squeeze risk. Funding Rate: Positive funding means longs pay shorts; extreme positive funding often precedes mean-reversion down. Liquidations: Forced closes at margin breach; cluster maps identify likely cascade zones.
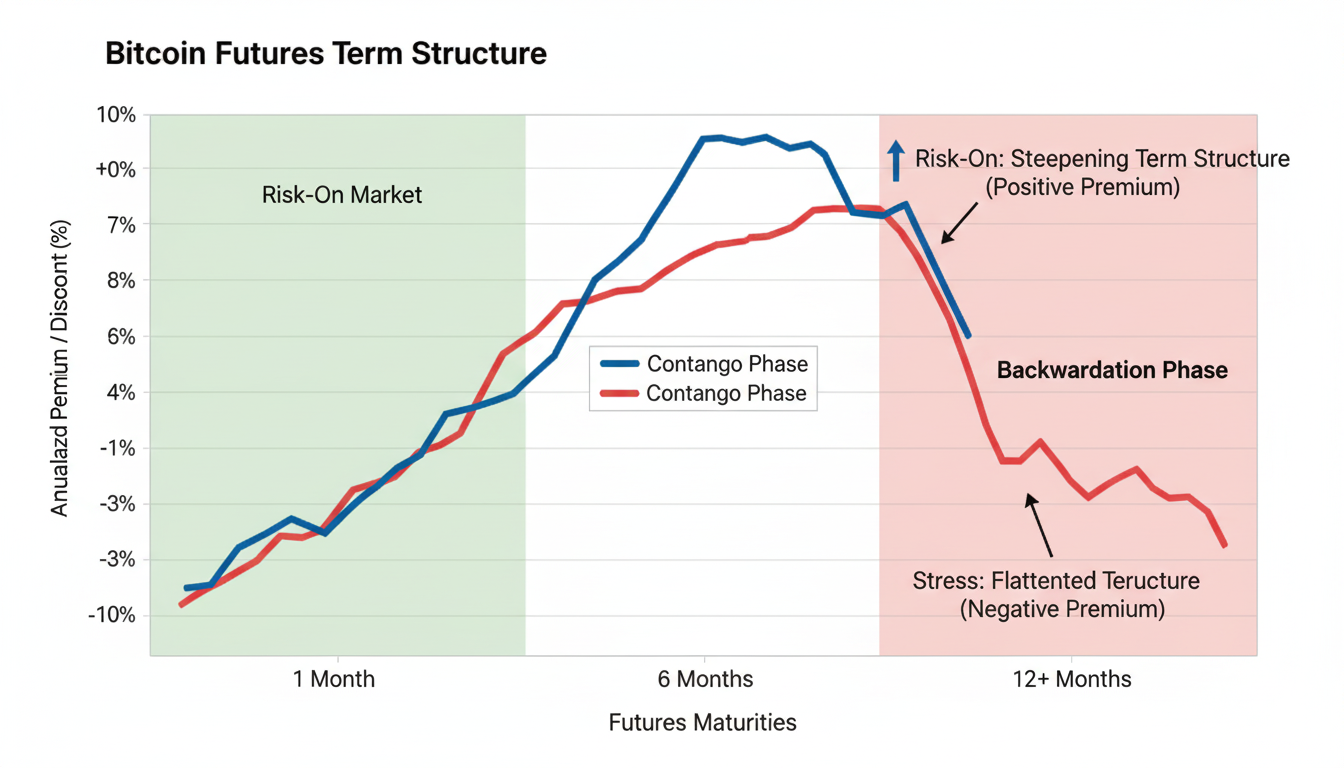
Spot–Futures Spreads (Contango & Backwardation)
Quarterlies typically trade at a premium (contango) in risk-on regimes, creating basis for carry trades. Discounts (backwardation) imply stress or risk-off conditions and can precede reversals.
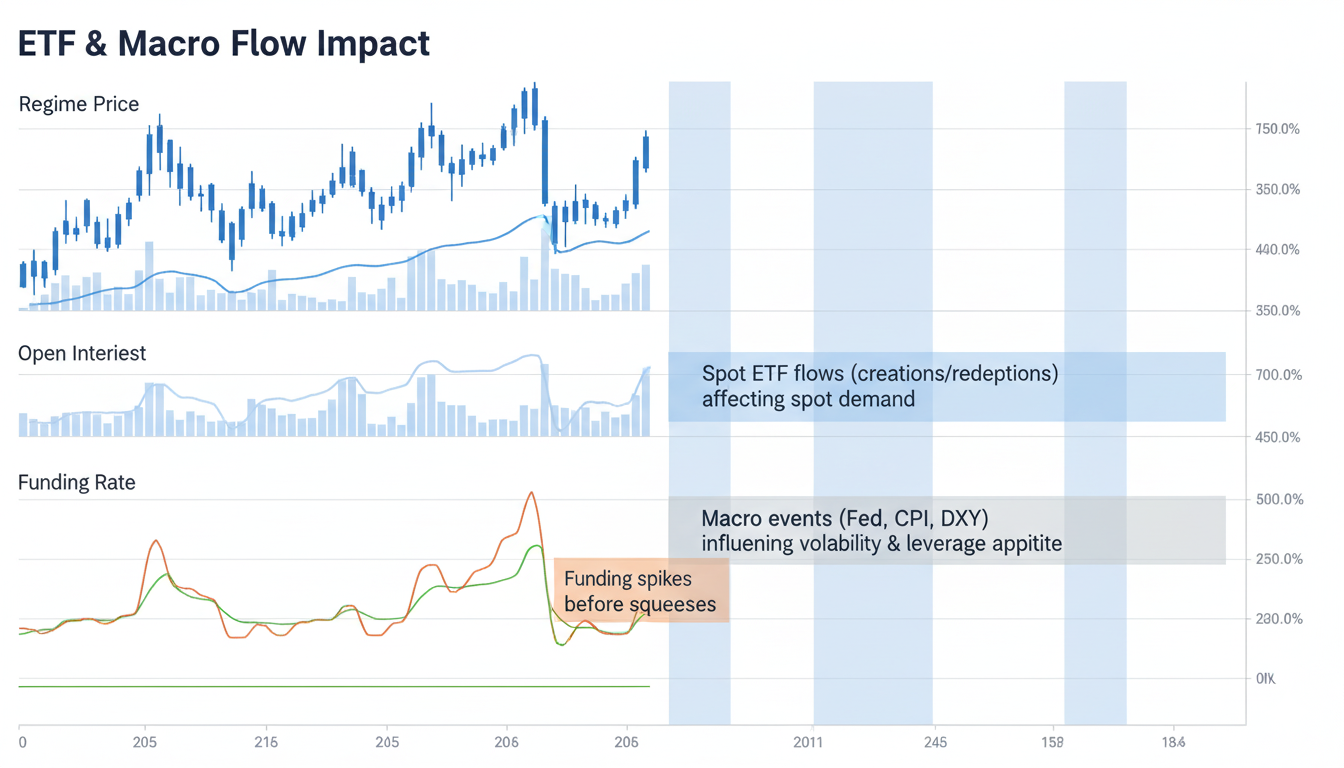
ETF & Macro Flow Impact
Spot ETF creations/redemptions shift net spot demand and can alter basis and perp funding regimes. Macro events (Fed decisions, CPI, DXY) drive cross-asset beta, changing BTC’s volatility and leverage appetite.
Bitcoin Futures Trading Strategies
1) Trend-Following Breakouts
Trade breakouts from consolidations with volatility filters (e.g., ATR, range compression). Confirm with rising OI and neutral/turning funding. Invalidation sits inside the prior range; scale out into measured move targets.
2) Mean-Reversion Around Funding Extremes
Fade crowded positioning when funding reaches extreme positive/negative levels and price deviates from VWAP or 20–50 MA. Require evidence: absorption in order flow, declining aggressive taker pressure, and a weakening delta trend.
3) Basis (Spot vs Futures) Carry
Buy spot and short equivalent futures when quarterly premium is attractive (annualized). Profit comes from the convergence of future to spot into expiry. Risk: premium compression, borrow costs, and exchange execution/fees.
4) Calendar Spreads
Long near-term/short far-term or vice versa based on term-structure shifts (contango steepening, backwardation flattening). Catalyst windows: pre-/post-monthly OPEX, quarterly roll, macro prints.
5) Options-Flow-Informed Futures Plays
Watch 25-delta skew, IV term structure, and gamma “walls.” Dealer hedging around large strikes often pins price or accelerates moves through key levels; futures volume surges reinforce the direction.
6) Cross-Exchange Arbitrage & Fee Engineering
Exploit price/ funding differences across venues. Net PnL hinges on maker rebates, taker fees, borrow rates, funding schedule, and latency. Use API or low-latency UIs and strict position/venue limits.
Exchange Comparison: Fees, Leverage & Perp Features
| Exchange | Max Leverage | Maker / Taker | Funding Interval | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance Futures | Up to 125x* | Rebates/tiers* | ~8h | Deep books; broad perp pairs. |
| Bybit | Up to 100x* | Tiered* | ~8h | Robust UI; active derivatives base. |
| OKX | Up to 100x* | Tiered* | ~8h | Strong risk controls; options suite. |
| CME (Institutional) | Exchange-set | Exchange-set | N/A (quarterlies) | Regulated; distinct session gaps. |
*Check current tiers and leverage caps by region/KYC level on the exchange.
Advanced On-Chain & Derivatives Signals
Whales, Miners, and Exchange Flows
- Whales: Large spot inflows/outflows often front-run perp squeezes.
- Miners: Distribution or hedging pressure can steepen discounts; watch miner balances and sell peaks.
- Stablecoins: Net inflows (USDT/USDC) to exchanges add fresh leverage capacity.
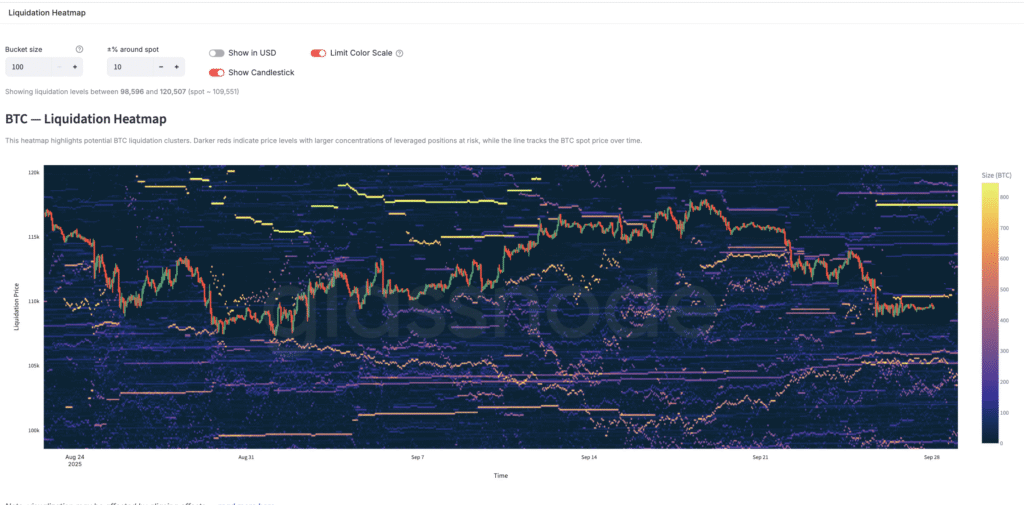
Liquidation Heatmaps & CVD
Heatmaps identify price zones with dense leverage. Positive CVD with failing price = absorption (possible reversal). Negative CVD with rising price = short covering risk; mind trailing stops.
CME vs Offshore Dynamics
CME share gains suggest institutional participation. Weekend “CME gaps” often become magnets early week; size entries around liquidity and upcoming catalysts to avoid whipsaws.
Risk Management for High-Leverage BTC Futures
Position Sizing & Volatility Targeting
Define risk in USD per trade (e.g., 0.5–1.0% of equity). Use ATR or rolling volatility to size contracts so a typical stop (e.g., 1.5× ATR) aligns with your risk budget. Avoid fixed leverage; let volatility guide size.
Margin Type, Liquidation, and Collateral Choice
- Isolated: Caps risk to the single position; safer for discrete trades.
- Cross: Shares margin across positions; use only with robust hedging discipline.
- Collateral: Using USD/stablecoin reduces directional collateral risk vs coin-margined.
Funding Cost Control
Persistent positive funding erodes long PnL; mitigate via timing (enter after settlements), hedges (options/counter-venue), or rotating to quarterlies when perp funding spikes.
Pre-Mortem & Rule-Set
Write rules before the trade: entry criteria, invalidation, partials, hard stop, and “max pain” daily drawdown. No averaging-down without a new, independent signal.
Macro Events That Shape BTC Futures
Fed, CPI, and USD Liquidity
Higher real yields and a stronger dollar tend to compress risk appetite and basis. Align risk with the macro calendar: pre-event de-leverage; post-event momentum or mean-reversion depending on surprise.
BTC Dominance & Alt Rotation
Rising dominance concentrates liquidity in BTC perps; falling dominance signals rotation to alts and thinner BTC trend persistence. Adjust leverage and take-profit structure accordingly.
Session Microstructure (Asia, EU, US)
Asia often sets overnight tone; EU adds liquidity; US drives event-risk. Many squeezes expand during session overlaps; plan entries around these windows.
Halving Cycles & Long-Term Futures Impact
Post-halving supply dynamics can elevate term-structure premiums in risk-on regimes; however, distribution from long-term holders near cycle highs can flatten or invert the curve unexpectedly—defend with stops.
Tools & Dashboards for BTC Futures Traders
- Charting & Execution: TradingView, exchange native ladders, depth/DOM.
- Derivatives Data: OI, funding, liquidation maps, basis matrix, CVD/Delta by venue.
- On-Chain: Exchange netflows, stablecoin supplies, whale/miner trackers.
- Automation: Rule-based alerts, position bots, risk dashboards.
FAQs — Bitcoin Futures Trading (2025)
Is Bitcoin Futures Trading Profitable?
Yes, but only with edge and risk control. Profitability comes from repeatable setups (e.g., basis carry, breakout+OI confirmation, funding extremes) and disciplined risk sizing. Without rule-sets, leverage magnifies errors.
What Are The Biggest Risks With High Leverage?
Forced liquidation and behavioral errors. Thin liquidity, sudden funding spikes, or news shocks can gap past stops. Keep leverage dynamic, size with volatility, and set hard daily loss limits.
How Do Funding Rates Affect PnL?
Funding adds/subtracts carry on perp positions. Longs pay when funding > 0; shorts pay when < 0. In strong trends, price return can dominate funding; in chop, funding can erode PnL quickly.
Which Exchange Is Best For Beginners?
Pick deep liquidity, transparent fees, and robust risk tools. Test on testnet or low size, learn order types, and verify liquidation mechanics.
Quick Matrix: Strategy → Confirmation Signals
| Strategy | Core Signal | Risk Control | Common Mistake |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakout Trend | Range break + OI ↑ + neutral/turning funding | Stop inside range; trail with structure | Chasing late; ignoring session overlaps |
| Funding Fade | Extreme funding + delta exhaustion | Tight stop beyond wick cluster | Fading strong trend without reversal prints |
| Basis Carry | Quarterly premium (annualized) attractive | Hedge size = spot size; monitor borrow | Ignoring fee/borrow/funding drag |
| Calendar Spread | Term-structure shift (steepen/flatten) | Independent legs; hard time stop | Holding through OPEX/roll without plan |
Trade Responsibly: Derivatives are high risk. Never risk funds you cannot afford to lose. Consider paper trading or minimal size until your rules show consistency.
Affiliate Disclosure: Some links may be affiliate links; we may earn a commission at no extra cost to you. We only recommend platforms we believe provide value to readers.
| Exchange | Taker Fee % / Rebate | Maker Fee % / Rebate | Funding Rate Example (positive/negative) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | 0.04% | 0.02% | VIP Tiers, BNB Discount | |
| Bybit | 0.055% | –0.02% | Tiered Rebates | |
| OKX | –0.3% | –0.25% | Volume Discounts | |
| Deribit | –0.07% | –0.01% | Variable | |
Updated: October 3, 2025
